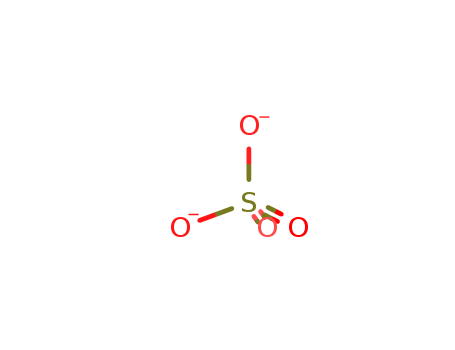
- Chemical Name:SULFATE STANDARD
- CAS No.:14808-79-8
- Molecular Formula:O4S-2
- Molecular Weight:96.0636
- Hs Code.:
- European Community (EC) Number:604-622-9
- UNII:7IS9N8KPMG
- DSSTox Substance ID:DTXSID3042425
- Nikkaji Number:J215.795K
- Wikipedia:Sulfate ion
- Wikidata:Q172290
- NCI Thesaurus Code:C76207
- RXCUI:1426598
- Mol file:14808-79-8.mol
Synonyms:Sulfate(ion 2-);Sulfate anion;Sulfate anion(2-);Sulfate(2-);Sulfuric acid, ion(2-);Sulphate;Sulfate ion (SO42-);Sulfate ion;Sulfate dianion;sulfate;


 Xn
Xn


