Base Information
Edit
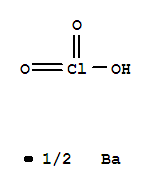
- Chemical Name:BARIUM CHLORATE MONOHYDRATE
- CAS No.:13477-00-4
- Molecular Formula:Ba. 2 Cl H O3
- Molecular Weight:304.24
- Hs Code.:2829199000
- Mol file:13477-00-4.mol
Synonyms:Bariumchlorate (6CI,7CI); Chloric acid, barium salt (8CI,9CI); Barium chlorate(Ba(ClO3)2)