- Chemical Name:Magnesium Hydroxide
- CAS No.:1309-42-8
- Deprecated CAS:13760-51-5,1395893-88-5
- Molecular Formula:H2MgO2
- Molecular Weight:56.3038
- Hs Code.:2816.10
- European Community (EC) Number:215-170-3
- UNII:NBZ3QY004S
- DSSTox Substance ID:DTXSID4049662
- Nikkaji Number:J43.883I
- Wikipedia:Magnesium hydroxide
- Wikidata:Q407548
- NCI Thesaurus Code:C29262
- RXCUI:6581
- ChEMBL ID:CHEMBL1200718
- Mol file:1309-42-8.mol
Synonyms:Brucite;Hydrate, Magnesium;Hydroxide, Magnesium;Magnesium Hydrate;Magnesium Hydroxide;Magnesium Hydroxide (Mg(OH)4)


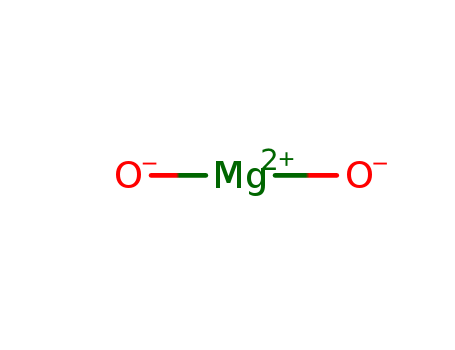
 Xi
Xi
 Xi:Irritant;
Xi:Irritant;

