- Quinoline
- Quinoline sulphate
- Quinoline Yellow
- Quinoline Yellow
- Quinoline Yellow WS
- Quinoline, 1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-1-(phenylsulfonyl)-
- Quinoline, 1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-6-nitro-
- Quinoline, 2-(2-chloroethylamino)-, hydrochloride
- Quinoline, 2,3-dibromo-
- Quinoline, 2,4-dichloro-7-methoxy-
- 91225-21-7Benzoic acid,4-(trans-4-butylcyclohexyl)-, 4-cyanophenyl ester
- 91225-40-02-Pyrazinamine,5-bromo-3-hydrazinyl-
- 91225-51-3Pyrazino[2,3-b]pyrazine,2-bromo-6-methyl-
- 912259-10-06,7-dihydro-1H-indazol-4(5H)-one
- 912259-11-16,6-dimethyl-6,7-dihydro-1H-indazol-4(5H)-one
- 912265-91-9Isoxazolo[4,5-c]pyridine-3-carboxylicacid, 4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-, ethyl ester, hydrochloride (1:1)
- 91229-91-31,2-Pyrrolidinedicarboxylicacid, 5-oxo-, 1,2-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl) ester, (2S)-
- 912329-03-4Karavilagenin A
- 91233-70-45-Pyrimidinol,2-methoxy-
- 912342-10-0Benzoicacid, 4-[(1R)-1-aminoethyl]-, methyl ester
Hot Products
- 1185-53-1Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethanehydrochloride
- 147536-97-8Bosentan
- 34642-77-8Amoxicillin sodium
- 181289-33-8Hexanoic acid,3-(2-amino-2-oxoethyl)-5-methyl-, (3R)-
- 4965-33-77-Chloro-2-methylquinoline
- 79-94-7Phenol,4,4'-(1-methylethylidene)bis[2,6-dibromo-
- 91-00-9Benzenemethanamine,a-phenyl-
- 85006-31-12-Thiophenecarboxylicacid, 3-amino-4-methyl-, methyl ester
- 104987-11-3Tacrolimus
- 141-53-7Sodium formate
- 8001-54-5Quaternary ammonium compounds, alkylbenzyldimethyl, chlorides
- 9003-39-8Povidone
- 10161-34-9Trenbolone acetate
- 402957-28-2Telaprevir
- 68-19-9Cyanocobalamin

|
Basic Information |

|
Post buying leads |

|
Suppliers |

|
Cas Database |

| Name |
Quinoline |
EINECS | 202-051-6 |
| CAS No. | 91-22-5 | Density | 1.106 g/cm3 |
| PSA | 12.89000 | LogP | 2.23480 |
| Solubility | slightly soluble in water | Melting Point |
-17--13 °C(lit.) |
| Formula | C9H7N | Boiling Point | 234.1 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Weight | 129.161 | Flash Point | 101.1 °C |
| Transport Information | UN 2656 6.1/PG 3 | Appearance | colourless to brown liquid |
| Safety | 26-36/37/39-36-23 | Risk Codes | 21/22-38-41-68-40-37/38 |
| Molecular Structure |
|
Hazard Symbols |
 Xn Xn
|
| Synonyms |
1-Azanaphthalene;1-Benzazine;B 500;Benzo[b]pyridine;Benzopyridine;Leucol;Leucoline;Leukol;NSC 3396;Quinolin; |
Article Data | 497 |
Quinoline History
Quinoline was first extracted from coal tar in 1834 by Friedlieb Ferdinand Runge.
Quinoline Consensus Reports
Reported in EPA TSCA Inventory. EPA Genetic Toxicology Program. Community Right-To-Know List.
Quinoline Standards and Recommendations
DOT Classification: 6.1; Label: KEEP AWAY FROM FOOD
Quinoline Specification
1. Introduction of Quinoline
Quinoline is also named as 1-Azanaphthalene ; 1-Benzazine ; 2,3-Benzopyridine ; AI3-01241 ; B-500 ; Benzo(b)pyridine ; Benzopyridine ; Benzopyridine (VAN) ; Chinoleine; Chinolin; Chinolin [Czech]; Chinoline; Leucol ; Leukol ; Quinolin ; USAF EK-218. Quinoline is colourless to brown liquid with a peculiar odor. It is soluble in water. Contact may irritate to skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. It may be toxic by ingestion. Quinoline is hygroscopic. It absorbs as much as 22% water. Quinoline is sensitive to light and moisture. Quinoline darkens on storage. It is a weak base. A potentially explosive reaction may occur with hydrogen peroxide. Quinoline reacts violently with dinitrogen tetraoxide. It also reacts violently with perchromates. It is incompatible with (linseed oil + thionyl chloride) and maleic anhydride. Quinoline is also incompatible with strong oxidizers and strong acids. Quinoline can be unpredictably violent. Quinoline dissolves sulfur, phosphorus and arsenic trioxide. Quinoline may attack some forms of plastics. It is a preparative hazard. Vapors are irritating to nose and throat and may cause headaches, dizziness, and nausea if inhaled. Ingestion causes irritation of mouth and stomach; vomiting may occur.
2. Properties of Quinoline
Molecular Weight: 129.16 g/mol
Melting Point: −17-−13 °C(lit.)
Boiling Point: 234.1 °C at 760 mmHg
Flash Point: 101.1 °C
Density: 1.093 g/mL at 25 °C
Water Solubility: slightly soluble
Index of Refraction: 1.642
Molar Refractivity: 42.18 cm3
Molar Volume: 116.7 cm3
Surface Tension: 46.6 dyne/cm
XLogP3: 2
H-Bond Acceptor: 1
Exact Mass: 129.057849
MonoIsotopic Mass: 129.057849
Topological Polar Surface Area: 12.9
Heavy Atom Count: 10
3. Structure Descriptors of Quinoline
Canonical SMILES: C1=CC=C2C(=C1)C=CC=N2
InChI: InChI=1S/C9H7N/c1-2-6-9-8(4-1)5-3-7-10-9/h1-7H
InChIKey: SMWDFEZZVXVKRB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
EINECS: 202-051-6
Product Categories: PYRIDINE; Intermediates; Organics; Quinolinecarboxylic Acids, etc.; Quinolines
4. Toxicity of Quinoline
| 1. | skn-rbt 10 mg/24H open MLD | AMIHBC AMA Archives of Industrial Hygiene and Occupational Medicine. 4 (1951),119. | ||
| 2. | eye-rbt 250 µg open SEV | AMIHBC AMA Archives of Industrial Hygiene and Occupational Medicine. 4 (1951),119. | ||
| 3. | mma-sat 1 µmol/plate ABCHA6 42,861,78 | |||
| 4. | dnd-esc 30 µmol/L | MUREAV Mutation Research. 89 (1981),95. | ||
| 5. | mma-ham:ovr 80 µmol/L | ENMUDM Environmental Mutagenesis. 4 (1982),395. | ||
| 6. | sce-ham:ovr 110 µg/L | ENMUDM Environmental Mutagenesis. 7 (1985),1. | ||
| 7. | orl-rat LD50:331 mg/kg | 85JCAE Prehled Prumyslove Toxikologie; Organicke Latky Marhold, J.,Prague, Czechoslovakia.: Avicenum,1986,848. | ||
| 8. | ipr-mus LDLo:64 mg/kg | CBCCT* “Summary Tables of Biological Tests“ National Research Council Chemical-Biological Coordination Center. 2 (1950),190. | ||
| 9. | skn-rbt LD50:540 mg/kg | AMIHBC AMA Archives of Industrial Hygiene and Occupational Medicine. 4 (1951),119. | ||
| 10. | scu-rbt LDLo:200 mg/kg | HBAMAK “Abdernalden’s Handbuch der Biologischen Arbeitsmethoden.“ 4 (1935),1289. |
5. Safety Information of Quinoline
Poison by ingestion, subcutaneous, and intraperitoneal routes. Moderately toxic by skin contact. A skin and severe eye irritant. Mutation data reported. Questionable carcinogen with experimental neoplastigenic and tumorigenic data. It can cause retinitis similar to that caused by naphthalene but without causing opacity of the lens. Combustible when exposed to heat or flame. Its preparation has caused many industrial explosions. Potentially explosive reaction with hydrogen peroxide. Violent reaction with dinitrogen tetraoxide, perchromates. Incompatible with linseed oil + thionyl chloride, maleic anhydride. Unpredictably violent. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx.
Hazard Codes:
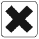 Xn
Xn Risk Statements: 21/22-38-41-68-40-37/38
21/22: Harmful in contact with skin and if swallowed
38: Irritating to the skin
41: Risk of serious damage to eyes
68: Possible risk of irreversible effects
40: Limited evidence of a carcinogenic effect
37/38: Irritating to respiratory system and skin
Safety Statements: 26-36/37/39-36-23
26: In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice
36/37/39: Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection
36: Wear suitable protective clothing
23: Do not breathe gas/fumes/vapor/spray (appropriate wording to be specified by the manufacturer)
RIDADR: UN 2656 6.1/PG 3
WGK Germany: 2
RTECS: VA9275000
F: 8: Photosensitive.
HazardClass: 6.1
PackingGroup: III
6. Preparation ofQuinoline
Quinoline can be synthesized using various methods:
1.Camps quinoline synthesis utilizing an o-acylaminoacetophenone and hydroxide
2.Knorr quinoline synthesis, using a β-ketoanilide and sulfuric acid.
3.Gould-Jacobs reaction starting from an aniline and ethyl ethoxymethylenemalonate
4.Niementowski quinoline synthesis, using anthranilic acid and ketones.
5.Combes quinoline synthesis using anilines and β-diketones.
6.Conrad-Limpach synthesis using anilines and β-ketoesters.
7.Doebner-Miller reaction using anilines and α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds.
8.Friedländer synthesis using 2-aminobenzaldehyde and acetaldehyde.
9.Skraup synthesis using ferrous sulfate, glycerol, aniline, nitrobenzene, and sulfuric acid.
10.Povarov reaction using an aniline, a benzaldehyde and an activated alkene.
7. Use of Quinoline
Quinoline is mainly used as a building block to other specialty chemicals. It is used as reagents in organic synthesis, alkaline condensing agent and solvent.

