
Journal of the American Chemical Society p. 3726 - 3730 (1986)
Update date:2022-08-17
Topics:
 Smith, Richard H.
Smith, Richard H.
 Denlinger, Cheryl L.
Denlinger, Cheryl L.
 Kupper, Robert
Kupper, Robert
 Mehl, Andrew F.
Mehl, Andrew F.
 Michejda, Christopher J.
Michejda, Christopher J.
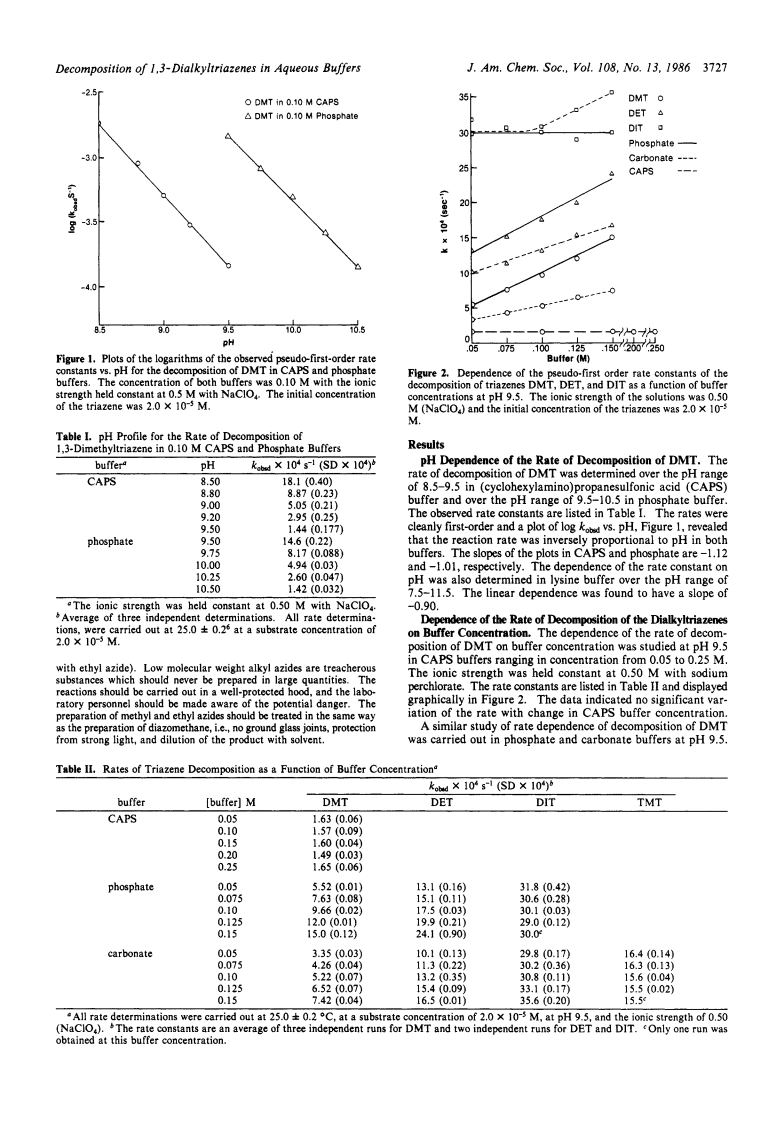
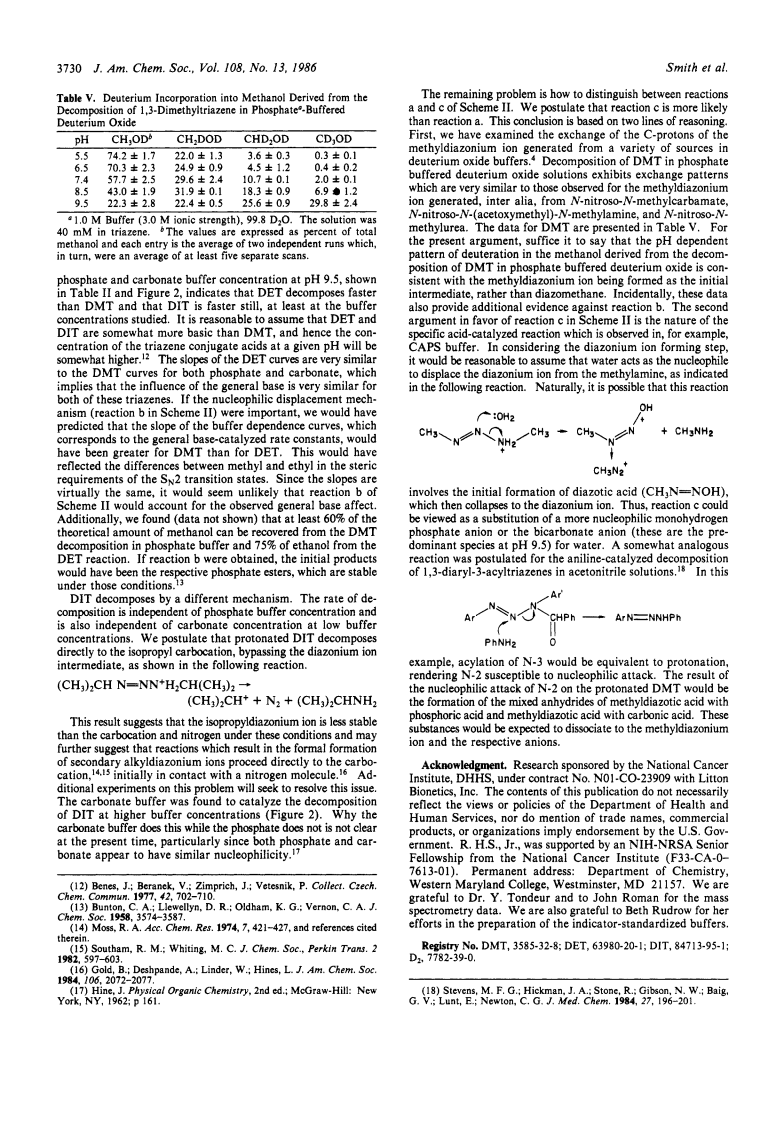
1,3-Dialkyltriazenes, prepared by the reaction of alkyl azides with alkyllithiums, are stable as pure liquids or in aprotic solutions.The kinetics of decomposition of 1,3-dimethyltriazene (DMT) were investigated in buffered, aqueous solutions over the pH range of 9-12.The reaction is acid-catalyzed since the rate is inversely proportional to pH.The invariance of the rate with (cyclohexylamino)propanesulfonic acid (CAPS) buffer concentration at pH 9.5 and the finding of an inverse solvent isotope effect of 0.35 suggest that the reaction follows simple specific acid catalysis in that buffer.Decomposition of DMT in phosphate and carbonate buffers, however, indicated dependence of rate on buffer concentration, although the solvent isotope effects were still less than 1.These data suggested that the reaction in those buffers is catalyzed by specific acid, followed by general base.The kinetics of decomposition of 1,3-diethyltriazene (DET) and 1,3-diisopropyltriazene (DIT) were also studied.DET decomposed slightly more rapidly than DMT in phosphate and carbonate buffers but showed a similar dependence of the rate on the buffer concentration.This triazene also exhibited an inverse solvent isotope effect.DIT, on the other hand, showed a rate that was invariant with phosphate buffer concentration and exhibited a biphasic profile of rate vs. carbonate buffer concentration.The rate of decomposition of DIT was also invariant with the pKa of various buffers and showed an inverse solvent isotope effect.Decomposition of DMT in buffered deuterium oxide resulted in incorporation of deuterium into the product methanol, which indicated that an intermediate product of the reaction was the methyldiazonium ion.The dependence of the rate of decomposition on buffer concentration of DMT and DET is explained in terms of nucleophilic attack of buffer anions on N-2 of the protonated triazenes.The proponated DIT, on the other hand, is seen as dissociating directly to the isopropyl carbonium ion in phosphate buffer and in low concentrations of carbonate buffer.
View More


Contact:86-28-61993785
Address:No.70-13-21, North Section, Erhuan
Shanghai AoBo Bio-Pharmaceutical Technology Co., Ltd.
Contact:+86-21-51320130-801, 816
Address:Room 601, No. 1011, Halei Road, Zhangjiang High-Tech Park, Pudong, Shanghai
qingcang(shanghai) Medical Technology Co., Ltd.
Contact:021-58099007
Address:shanghai
Contact:86-371-63655023
Address:No.85,jinshui road,zhengzhou,China
XI'AN CHUKANG BIOTECHNOLOGY CO.,LTD
Contact:29-63685658 63685359
Address:Room 3-1202,Building 1,Oriental oasis,East of Xianning Road,Xi'an,Shaanxi 710043 P.R.China
Doi:10.1021/jo00355a030
(1986)Doi:10.1166/jnn.2018.13941
(2018)Doi:10.1002/adsc.200900074
(2009)Doi:10.1021/jacs.6b01706
(2016)Doi:10.1134/S1070363220100242
(2020)Doi:10.1071/CH02003
(2001)