Radon
Radon General
| Name:Radon | Symbol:Rn |
| Type:Noble Gas | Atomic weight:222 |
| Density @ 293 K: 0.00973 g/cm3 | Atomic volume:50.5 cm3/mol |
|
Discovered:
Radon gas was discovered in 1900 by Fredrich E. Dorn. He described it as radium emanation because it arose from the element radium, which he was working with. In 1908 William Ramsay and Robert Gray isolated the gas and named it niton. Since 1923, it has been called radon (after radium, one of its sources). Radon was one of the earliest discovered radioactive elements, identified after uranium, thorium, polonium and radium. |
|
Radon States
| State (s, l, g):gas | |
| Melting point:202 K (-71 °C) | Boiling point:211 K (-62 °C) |
Radon Energies
| Specific heat capacity:0.09 J g-1 K-1 | Heat of atomization:0 kJ mol-1 |
| Heat of fusion:2.890 kJ mol-1 | Heat of vaporization :16.40 kJ mol-1 |
| 1st ionization energy: 1037 kJ mol-1 | 2nd ionization energy: kJ mol-1 |
| 3rd ionization energy: kJ mol-1 | Electron affinity: kJ mol-1 |
Radon Oxidation & Electrons
| Shells:2,8,18,32,18,8 | Electron configuration:[Xe] 4f14 5d10 6s2 6p6 |
| Minimum oxidation number:0 | Maximum oxidation number:0 |
| Min. common oxidation no.:0 | Max. common oxidation no.:0 |
| Electronegativity (Pauling Scale): | Polarizability volume:5.3 Å3 |
Radon Appearance & Characteristics
| Structure: | Color:colorless |
| Hardness: mohs | |
|
Harmful effects:
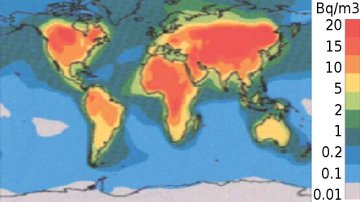
Radon is highly radioactive and a carcinogen. Its decay products are toxic and radioactive. Radon is present in most homes and is the number one cause of lung-cancer in non-smokers in the USA. (See video on left.) |
|
|
Characteristics:
Radon is one of the noble gases; hence it is a chemically inert, monatomic gas. It is also radioactive, colorless and odorless. Uses: Radon was used for treating cancer by radiotherapy. Safer treatments are now available. |
|
Radon Reactions
| Reaction with air:none | Reaction with 6 M HCl:none |
| Reaction with 15 M HNO3:none | Reaction with 6 M NaOH:none |
Radon Compounds
| Oxide(s): | Chloride(s): |
| Hydride(s): |
Radon Radius
| Atomic radius:pm | Ionic radius (1+ ion):pm |
| Ionic radius (2+ ion):pm | Ionic radius (3+ ion):pm |
| Ionic radius (2- ion):pm | Ionic radius (1- ion):pm |
Radon Conductivity
| Thermal conductivity:3.61 W m-1 K-1 | Electrical conductivity:x 10-6 S m-1 |
Radon Abundance & Isotopes
| Abundance earth's crust:4 x10-13milligrams per kilogram | |
| Abundance solar system:parts per billion by weight, part per billion by moles | |
| Cost, pure:$ per 100g | |
| Cost, bulk:$ per 100g | |
|
Source:
Radon is produced naturally by the radioactive decay of uranium and other elements, such as radium. For example, 222Rn is produced by the decay of radium (226Ra). |
|
|
Isotopes:
Radon has 33 isotopes whose half-lives are known, with mass numbers 196 to 228. None are stable. The most stable isotope is 222Rn, with a half-life of 3.8 days. |
|
Radon Other
|
Other:
|
|
Prev: Astatine Next: Francium |