10.1016/j.jorganchem.2003.08.043
The research delves into the stereochemistry of [MBr(CO)3L2] complexes with M being either manganese (Mn) or rhenium (Re) and L representing triorganophosphine ligands. The study encompasses the synthesis, characterization, and structural analysis of these complexes, which are pivotal in organometallic chemistry. The researchers synthesized a variety of these complexes and employed elemental analysis, infrared (IR) spectroscopy, and 31P-nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy for their characterization. The synthesis was executed based on a literature method, involving reactions in chloroform with different durations for Mn and Re complexes. To determine the stereochemistry, the researchers conducted single-crystal X-ray diffraction studies on select complexes, confirming the fac,cis geometries for Re(I) derivatives and those with bidentate ligands, and mer,trans geometries for the remaining Mn(I) derivatives. Additionally, IR spectroscopy was instrumental in analyzing the carbonyl stretching regions, aiding in the stereochemical assignments, while 31P-NMR provided insights into the ligand coordination to the metal center. This comprehensive approach underscored the reliability of single-crystal X-ray diffraction in confirming the stereochemistry, especially when compared to the potential inaccuracies of IR spectroscopy-based assignments.


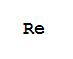
 F,
F,  C
C
