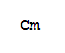Chemical Property of Curium
Edit
Chemical Property:
- Melting Point:1345°
- Boiling Point:bp (calc) 3110°
- PSA:0.00000
- Density:13.51; d 12.9
- LogP:0.00000
- Hydrogen Bond Donor Count:0
- Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count:0
- Rotatable Bond Count:0
- Exact Mass:247.07035
- Heavy Atom Count:1
- Complexity:0
- Purity/Quality:
-
99% *data from raw suppliers
CURIUM 95.00% *data from reagent suppliers
Safty Information:
- Pictogram(s):
- Hazard Codes:
- MSDS Files:
-
SDS file from LookChem
Useful:
- Chemical Classes:Physical/Radiation -> Radionuclides
- Canonical SMILES:[Cm]
- Recent ClinicalTrials:Extended-release Naltrexone and Care Management for Alcohol Dependent Frequent Emergency Department Users
-
Physical properties
After the discovery of plutonium and before elements 95 and 96 were discovered, theirexistence and properties were predicted. Additionally, chemical and physical properties werepredicted to be homologous (similar) to europium (63Eu) and gadolinium (64Gd), locatedin the rare-earth lanthanide series just above americium (95Am) and curium (96Cm) on theperiodic table. Once discovered, it was determined that curium is a silvery-white, heavymetal that is chemically more reactive than americium with properties similar to uraniumand plutonium. Its melting point is 1,345°C, its boiling point is ~1,300°C, and its density is13.51g/cm3.
-
Uses
242Cm and 244Cm as power sources in radionuclide batteries for space and medical applications. 242Cm as radioactive heat source. 248Cm in accelerator studies to form superheavy elements. There are no major commercial uses for curium because of the extremely small amountproduced. In the future, the most important use of curium may be to provide the power forsmall, compact thermoelectric sources of electricity, by generating heat through the nucleardecay of radioisotope curium-241. These small, efficient power sources can be used in individualhomes or remote regions to provide electricity to areas that cannot secure it from othersources. It could also be used as a source of electricity in spacecraft. However, today curium’smain use is for basic scientific laboratory research.