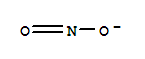10.1016/j.tetlet.2018.03.066
The research aims to develop selective anion receptors that utilize weak C-H hydrogen bonds, with a focus on phosphinate receptors. Phosphinates are significant in nature due to their association with metabolic diseases and conditions like obesity, NASH, hypercholesterolemia, and diabetes. The researchers designed and synthesized three receptors (1, 2, and 3) that utilize both amide N-H and alpha C-H (Cα-H) to the carbonyl group, differing in the substituent group attached to the alpha carbon, which affects the polarity of the CαH bond and thus the strength of association with anion guests. The study concluded that host 3, with a positively charged pyridinium group, showed the highest binding affinity due to the increased polarity of the Cα-H bond, demonstrating the importance of C-H hydrogen bonding as a modulating element for anionic recognition. Key chemicals used in the synthesis include 1,2-phenylenediamine, acetic acid, cyanoacetic acid, chloroacetyl chloride, pyridine, and various anions for testing, such as dimethyl phosphinate, benzoate, nitrite, and others.