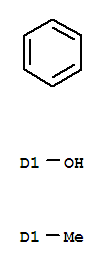
- Chemical Name:P-Cresol
- CAS No.:1319-77-3
- Molecular Formula:C7H8O
- Molecular Weight:108.15
- Hs Code.:29071219
- European Community (EC) Number:203-398-6
- ICSC Number:0031
- NSC Number:756709,95259,3696
- UN Number:2076,3455
- UNII:1MXY2UM8NV
- DSSTox Substance ID:DTXSID7021869
- Nikkaji Number:J1.185A
- Wikipedia:P-Cresol
- Wikidata:Q312251,Q83056691,Q83118968
- NCI Thesaurus Code:C61880
- RXCUI:2467144
- Pharos Ligand ID:8HBUAKMT3JC1
- Metabolomics Workbench ID:37894
- ChEMBL ID:CHEMBL16645
- Mol file:1319-77-3.mol
Synonyms:4-cresol;4-cresol, aluminum salt;4-cresol, potassium salt;4-cresol, sodium salt;4-methylphenol;p-cresol;para-cresol


 T
T
