10.1055/s-0036-1589089
The study presents a novel method for synthesizing N,N-disubstituted hydroxylamines from secondary amines using choline peroxydisulfate (ChPS) as an oxidizing agent. ChPS, a task-specific ionic liquid, is synthesized from choline chloride and potassium persulfate. It acts as an environmentally benign and biodegradable oxidant, enabling the selective oxidation of a wide variety of secondary amines to their corresponding hydroxylamines in a rapid, one-step reaction under mild conditions (RT to 60 °C for 1 hour). The method is notable for its operational simplicity, high selectivity, and green reaction conditions. The study explores the oxidation of various secondary amines, including aliphatic, aromatic, and heterocyclic compounds, yielding N,N-disubstituted hydroxylamines in moderate to good yields (up to 96%). The products are characterized using 1H NMR and 13C NMR spectroscopy. The proposed mechanism involves nucleophilic attack by the secondary amine on ChPS, leading to the cleavage of O–O and O–S bonds and the formation of hydroxylamines. This method is particularly useful for oxidizing complex amines and offers a practical and efficient alternative to traditional oxidation methods, which often suffer from issues such as reagent instability, low yields, and harsh reaction conditions.
10.1021/acscatal.9b02512
The research presented in the "ACS Catalysis" article focuses on the Rh(III)-catalyzed regioselective C?H amidation of N-methoxy-1H-indole-1-carboxamides by 1,4,2-dioxazol-5-ones, exploring how the directing group (DG), specifically the N-methoxy amide, influences the reaction's outcome. The study experimentally and computationally investigates the chameleon-like behavior of the DG under various conditions, leading to four distinct transformation pathways: DG-retained, DG-coupled, DG-eliminated, and DG-migrated processes. The experiments involved using [Cp*RhCl2]2 and Zn(OTf)2 as catalysts, with NaOAc as a base and solvents like DCE and THF, alongside the addition of water and K2S2O8 under different temperatures to achieve selective transformations. The analyses included optimization of reaction conditions, substrate scope evaluation, and mechanistic studies through DFT calculations, which provided insights into the reaction mechanisms and the role of the N-methoxy amide DG in the regioselective C?H amidation process.
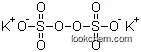


 O,
O, Xn
Xn
