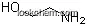Products Categories
| CAS No.: | 134-49-6 |
|---|---|
| Name: | PHENMETRAZINE |
| Article Data: | 22 |
| Molecular Structure: | |
|
|
|
| Formula: | C11H15NO |
| Molecular Weight: | 177.246 |
| Synonyms: | 2-Phenyl-3-methylmorpholine;2-Phenyl-3-methyltetrahydro-1,4-oxazine;3-Methyl-2-phenylmorpholine;3-Methyl-2-phenyltetrahydro-2H-1,4-oxazine;Oxazimedrine;Phenmetrazin;Phenmetrazine;Probese-P;Psychamine A 66; |
| EINECS: | 205-143-4 |
| Density: | 0.997 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point: | 285.2 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point: | 112.7 °C |
| PSA: | 21.26000 |
| LogP: | 2.06480 |
- 144851-82-1METHYL2-AMINO-3-FLUOROBENZOATE
- 483366-12-7(2S,4R)-1-Boc-2-cyano-4-hydroxypyrrolidine
- 173606-50-3BOC-10-AMINODECANOIC ACID
- 361456-36-2METHYL (R)-(+)-ISOCYANATO-3-PHENYLPROPI&
- 5156-58-1N-(1-Benzyl-4-pipperidinyl)-N-phenylpropanamide HCl
- 81281-59-67-Benzylideneaminotheophylline
- 50288-62-5threo-Phenyl-2-piperidyl acetamide
- 82993-81-5D-threo-Ritalinic acid hydrochloride
- 47087-37-6Z-D-Glu-OMe
- 73441-42-6METHYL-5-CHLORO-2,2-DIMETHYLVALERATE
 This product is a nationally controlled contraband, and the Lookchem platform doesn't provide relevant sales information.
This product is a nationally controlled contraband, and the Lookchem platform doesn't provide relevant sales information.
History
Phenmetrazine was first patented in Germany in 1952 by Boehringer-Ingelheim, with some pharmacological data published in 1954. It was the result of a search by Thomä and Wick for an anorectic drug without the side-effects of amphetamine.Phenmetrazine was introduced into clinical use in 1954 in Europe.Phenmetrazine (Preludin) is a stimulant drug of the morpholine chemical class that was previously used as an appetite suppressant.It was initially replaced by its analogue phendimetrazine which functions as a prodrug to phenmetrazine, but now it is rarely prescribed either, due to concerns of abuse and addiction.
Specification
The Preludin, with the CAS registry number 134-49-6, is also known as Phenmetrazine. Its EINECS registry number is 205-143-4. This chemical's molecular formula is C11H15NO and molecular weight is 177.24. Its IUPAC name is called 3-methyl-2-phenylmorpholine. What's more, this chemical's classification codes are Anti-Obesity Agents; Appetite Depressants; Autonomic Agents; Central Nervous System Agents; Central Nervous System Stimulants; Human Data; Peripheral Nervous System Agents; Sympathomimetics. Preludin is a stimulant drug of the morpholine chemical class that was previously used as an appetite suppressant, but has since been withdrawn from the market. In clinical use, Preludi produces less nervousness, hyperexcitability, euphoria and insomnia than drugs of the amphetamine family.
Physical properties of Preludin: (1)ACD/LogP: 1.53; (2)ACD/LogD (pH 5.5): -1.26; (3)ACD/LogD (pH 7.4): 0.33; (4)ACD/BCF (pH 5.5): 1; (5)ACD/BCF (pH 7.4): 1; (6)ACD/KOC (pH 5.5): 1; (7)ACD/KOC (pH 7.4): 10.13; (8)#H bond acceptors: 2; (9)#H bond donors: 1; (10)#Freely Rotating Bonds: 1; (11)Index of Refraction: 1.503; (12)Molar Refractivity: 52.55 cm3; (13)Molar Volume: 177.7 cm3; (14)Surface Tension: 34.3 dyne/cm; (15)Density: 0.997 g/cm3; (16)Flash Point: 112.7 °C; (17)Enthalpy of Vaporization: 52.43 kJ/mol; (18)Boiling Point: 285.2 °C at 760 mmHg; (19)Vapour Pressure: 0.00284 mmHg at 25°C.
Preparation of Preludin: this chemical can be prepared by 2-bromo-1-phenyl-propan-1-one and 2-amino-ethanol. This reaction will need reagent 99percent HCO2H. The reaction time is 20 hours with reaction temperature of 180 °C. The yield is about 80%.

Uses of Preludin: it can be used to produce 2,4-dimethyl-3-(3-methyl-2-phenyl-morpholinomethyl)-1-phenyl-3-pyrazolin-5-one. The yield is about 81%.

You can still convert the following datas into molecular structure:
(1)Canonical SMILES: CC1C(OCCN1)C2=CC=CC=C2
(2)InChI: InChI=1S/C11H15NO/c1-9-11(13-8-7-12-9)10-5-3-2-4-6-10/h2-6,9,11-12H,7-8H2,1H3
(3)InChIKey: OOBHFESNSZDWIU-UHFFFAOYSA-N
The toxicity data is as follows:
| Organism | Test Type | Route | Reported Dose (Normalized Dose) | Effect | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| man | TDLo | oral | 2857ug/kg (2.857mg/kg) | AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM: SYMPATHOMIMETIC | Therapie. Vol. 34, Pg. 205, 1979. |
| mouse | LD50 | intraperitoneal | 125mg/kg (125mg/kg) | SENSE ORGANS AND SPECIAL SENSES: OTHER: EYE BEHAVIORAL: EXCITEMENT BEHAVIORAL: IRRITABILITY | Arzneimittel-Forschung. Drug Research. Vol. 21, Pg. 1727, 1971. |
| mouse | LD50 | oral | 125mg/kg (125mg/kg) | Arzneimittel-Forschung. Drug Research. Vol. 23, Pg. 810, 1973. | |
| mouse | LD50 | subcutaneous | 195mg/kg (195mg/kg) | Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archiv fuer Experimentelle Pathologie und Pharmakologie. Vol. 222, Pg. 540, 1954. | |
| rat | LD50 | oral | 370mg/kg (370mg/kg) | Arzneimittel-Forschung. Drug Research. Vol. 23, Pg. 810, 1973. |