Products Categories
| CAS No.: | 38194-50-2 |
|---|---|
| Name: | Sulindac |
| Article Data: | 20 |
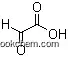
| Molecular Structure: | |
|
|
|
| Formula: | C20H17FO3S |
| Molecular Weight: | 356.418 |
| Synonyms: | 1H-Indene-3-aceticacid, 5-fluoro-2-methyl-1-[[4-(methylsulfinyl)phenyl]methylene]-, (Z)-;(Z)-5-Fluoro-2-methyl-1-[p-(methylsulfinyl)benzylidene]indene-3-acetic acid;Aflodac;Arthrocine;Artribid;Clinoril;Clisundac;Imbaral;MK 231;Mobilin;Reumofil;Reumyl;Sudac; |
| EINECS: | 253-819-2 |
| Density: | 1.38 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point: | 182-185 °C |
| Boiling Point: | 581.6 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point: | 305.6 °C |
| Solubility: | Soluble in water, methanol, ethanol. |
| Appearance: | yellow crystalline solid |
| Hazard Symbols: |
 Xn Xn
|
| Risk Codes: | 22-63-42/43 |
| Safety: | - |
| Transport Information: | UN 3249 |
| PSA: | 73.58000 |
| LogP: | 5.23120 |
- 483366-12-7(2S,4R)-1-Boc-2-cyano-4-hydroxypyrrolidine
- 5156-58-1N-(1-Benzyl-4-pipperidinyl)-N-phenylpropanamide HCl
- 81281-59-67-Benzylideneaminotheophylline
- 50288-62-5threo-Phenyl-2-piperidyl acetamide
- 82993-81-5D-threo-Ritalinic acid hydrochloride
- 47087-37-6Z-D-Glu-OMe
- 73441-42-6METHYL-5-CHLORO-2,2-DIMETHYLVALERATE
- 68439-39-4Poly(oxy-1,2-ethanediyl), alpha-(2-ethylhexyl)-omega-hydroxy-,
- 852475-26-4MC1568
- 43224-75-52,2,6,6-Tetramethyl-4-(2-propyleneoxy) Piperidine
- 2857-97-8Bromotrimethylsilane
- 84110-40-7Boronic acid,B-(2-methylpropyl)-
- 106-91-2Glycidyl methacrylate
- 7803-55-6Ammonium metavanadate
- 42252-34-6Carbamic chloride,N-ethyl-N-methyl-
- 22065-85-64-Piperidinecarboxaldehyde,1-(phenylmethyl)-
- 57090-45-61,2-Propanediol,3-chloro-, (2R)-
- 32221-81-1Glutamic acid, sodiumsalt (1:1)
- 104987-11-3Tacrolimus
- 141-53-7Sodium formate
- 8001-54-5Quaternary ammonium compounds, alkylbenzyldimethyl, chlorides
- 9003-39-8Povidone
- 10161-34-9Trenbolone acetate
- 402957-28-2Telaprevir
- 68-19-9Cyanocobalamin
Specification
The CAS registry number of Sulindac is 38194-50-2. The IUPAC name is 2-[(3Z)-6-fluoro-2-methyl-3-[(4-methylsulfinylphenyl)methylidene]inden-1-yl]acetic acid. In addition, the molecular formula is C20H17FO3S. What's more, it is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug which is derived from sulfinylindene. It is useful in the treatment of acute or chronic inflammatory conditions.
Physical properties about this chemical are: (1)ACD/LogP: 3.59; (2)ACD/LogD (pH 5.5): 2.33; (3)ACD/LogD (pH 7.4): 0.55; (4)ACD/BCF (pH 5.5): 17.3; (5)ACD/BCF (pH 7.4): 1; (6)ACD/KOC (pH 5.5): 117.35; (7)ACD/KOC (pH 7.4): 1.94; (8)#H bond acceptors: 3; (9)#H bond donors: 1; (10)#Freely Rotating Bonds: 4; (11)Polar Surface Area: 62.58 Å2; (12)Index of Refraction: 1.672; (13)Molar Refractivity: 96.22 cm3; (14)Molar Volume: 256.7 cm3; (15)Polarizability: 38.14 ×10-24cm3; (16)Surface Tension: 65.9 dyne/cm; (17)Density: 1.38 g/cm3; (18)Flash Point: 305.6 °C; (19)Enthalpy of Vaporization: 91.48 kJ/mol; (20)Boiling Point: 581.6 °C at 760 mmHg; (21)Vapour Pressure: 2.27E-14 mmHg at 25°C.
Preparation of Sulindac: At first, 5-fluorine-2-methyl-3-oxo-2,3-dihydro-1H-indene can react with 2-nitrilylacetic acid to give a product(Ⅰ) through condensation reaction. Then the Sulindac can be prepared by reacting product(Ⅰ) with p-methylthiobenzaldehyde through condensation and oxidation reaction.
.jpg)
Uses of Sulindac: it may be used in the treatment of preterm labor. In addition, it can react with N-hydroxy-succinimide to get [6-fluoro-3-(4-methanesulfinyl-benzylidene)-2-methyl-3H-inden-1-yl]-acetic acid 2,5-dioxo-pyrrolidin-1-yl ester. This reaction will need reagent DCC and solvent tetrahydrofuran. The reaction time is 1 hour at reaction temperature of 0 °C. The yield is about 35%.
![Sulindac can react with N-hydroxy-succinimide to get [6-fluoro-3-(4-methanesulfinyl-benzylidene)-2-methyl-3H-inden-1-yl]-acetic acid 2,5-dioxo-pyrrolidin-1-yl ester](/UserFilesUpload/Uses of Sulindac.jpg)
When you are using this chemical, please be cautious about it as the following:
This chemical is harmful if swallowed. And it may cause sensitization by inhalation and skin contact. Moreover, it may has risk of harm to the unborn child. Besides, it should not be used by persons with a history of major allergic reactions (urticaria or anaphylaxis).
You can still convert the following datas into molecular structure:
(1)SMILES: O=S(c1ccc(cc1)\C=C3/c2ccc(F)cc2\C(=C3C)CC(=O)O)C
(2)InChI: InChI=1/C20H17FO3S/c1-12-17(9-13-3-6-15(7-4-13)25(2)24)16-8-5-14(21)10-19(16)18(12)11-20(22)23/h3-10H,11H2,1-2H3,(H,22,23)/b17-9-
(3)InChIKey: MLKXDPUZXIRXEP-MFOYZWKCBF
The toxicity data is as follows:
| Organism | Test Type | Route | Reported Dose (Normalized Dose) | Effect | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| infant | LDLo | oral | 12mg/kg/2D-I (12mg/kg) | LUNGS, THORAX, OR RESPIRATION: OTHER CHANGES GASTROINTESTINAL: ULCERATION OR BLEEDING FROM STOMACH BLOOD: HEMORRHAGE | Acta Paediatrica. Vol. 85, Pg. 884, 1996. |
| man | TDLo | oral | 34mg/kg/6D-I (34mg/kg) | Journal of Rheumatology. Vol. 13, Pg. 1084, 1986. | |
| man | TDLo | oral | 43mg/kg/10D-I (43mg/kg) | LUNGS, THORAX, OR RESPIRATION: OTHER CHANGES LIVER: LIVER FUNCTION TESTS IMPAIRED BLOOD: LEUKOPENIA | JAMA, Journal of the American Medical Association. Vol. 244, Pg. 269, 1980. |
| man | TDLo | oral | 343mg/kg (343mg/kg) | BEHAVIORAL: CONVULSIONS OR EFFECT ON SEIZURE THRESHOLD VASCULAR: BP LOWERING NOT CHARACTERIZED IN AUTONOMIC SECTION BLOOD: "CHANGES IN SERUM COMPOSITION (E.G., TP, BILIRUBIN, CHOLESTEROL)" | Journal of Toxicology, Clinical Toxicology. Vol. 33, Pg. 173, 1995. |
| mouse | LD50 | intraperitoneal | 305mg/kg (305mg/kg) | Iyakuhin Kenkyu. Study of Medical Supplies. Vol. 13, Pg. 637, 1982. | |
| mouse | LD50 | oral | 507mg/kg (507mg/kg) | Drugs in Japan Vol. 6, Pg. APP-6, 1982. | |
| mouse | LD50 | subcutaneous | 398mg/kg (398mg/kg) | Iyakuhin Kenkyu. Study of Medical Supplies. Vol. 13, Pg. 637, 1982. | |
| rat | LD50 | intraperitoneal | 289mg/kg (289mg/kg) | Iyakuhin Kenkyu. Study of Medical Supplies. Vol. 13, Pg. 637, 1982. | |
| rat | LD50 | oral | 264mg/kg (264mg/kg) | Arzneimittel-Forschung. Drug Research. Vol. 30, Pg. 1398, 1980. | |
| rat | LD50 | subcutaneous | 336mg/kg (336mg/kg) | Iyakuhin Kenkyu. Study of Medical Supplies. Vol. 13, Pg. 637, 1982. | |
| women | LDLo | oral | 112mg/kg/2W-I (112mg/kg) | GASTROINTESTINAL: NAUSEA OR VOMITING LIVER: "HEPATITIS (HEPATOCELLULAR NECROSIS), DIFFUSE" | Journal of Rheumatology. Vol. 10, Pg. 512, 1983. |
| women | TDLo | oral | 8mg/kg/10H-I (8mg/kg) | BEHAVIORAL: ANOREXIA (HUMAN BEHAVIORAL: MUSCLE CONTRACTION OR SPASTICITY) GASTROINTESTINAL: "HYPERMOTILITY, DIARRHEA" | Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology. Vol. 8, Pg. 569, 1986. |