9004-65-3 Usage
Uses
Used in Food Industry:
Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose is used as a thickener, stabilizer, and emulsifier for syneresis control, texture enhancement, and to provide hot viscosity in various food products such as bakery goods, dressings, breaded foods, and salad dressing mix. The usage level ranges from 0.05 to 1.0%.
Used in Pharmaceutical Industry:
Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose is used as a viscosity modifier, film former, and stabilizer in pharmaceutical formulations, providing controlled release and improved drug delivery.
Used in Cosmetics Industry:
Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose is used as a thickening agent, emulsifier, and stabilizer in cosmetic products, enhancing the texture and providing a smooth consistency.
Used in Construction Industry:
Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose is used as a thickening agent, binder, and water retention agent in construction materials, improving the workability and performance of the final product.
Used in Textile Industry:
Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose is used as a thickening agent, stabilizer, and emulsifier in textile printing and dyeing processes, providing better color yield and improved fabric quality.
Used in Paper Industry:
Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose is used as a thickening agent, binder, and stabilizer in paper manufacturing, enhancing the paper's strength, smoothness, and printability.
Product features
Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose is propylene glycol ether of methyl cellulose, hydroxypropyl and methyl combine with anhydrous glucose ring by ether bond.It is white or pale white cellulose powder or particles. The characteristics of cold water dissolution and hot water insoluble are similar with methyl cellulose. Solubility in organic solvents is superior than water soluble, can be dissolved in anhydrous methanol and ethanol solution, also soluble in chlorinated hydrocarbons and ketones in organic solvents. Soluble in water, its water solution has a surface activity, the formation of the film after drying, heated and cooled, in turn, from the reversible conversion of sol to gel. Can be used alone in the cold drink, also can be used with other emulsifier, stabilizer. To cold drink, the maximum amount is 1%. Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose and other water-soluble high weight compounds use mixture, become transparent, higher viscosity. The gelation temperature of low viscosity products is higher than high viscosity of products. Its solution is stable at room temperature. In recent years, It has been widely used in petroleum chemical industry, papermaking, leather, textile printing and dyeing, pharmaceutical, food, cosmetics and other industries, and as the dispersing agent, thickening agent, adhesive, excipient, capsule, oil resistant coating and packing etc.
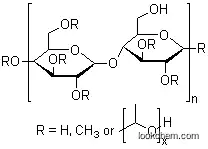
Figure 1 The molecular structure of hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose
Liquid Detergents
Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose and methyl cellulose are also water-soluble nonionic polymers. They are compatible with inorganic salts and ionic species up to a certain concentration. Methyl cellulose can be salted out of solution when the concentration of electrolytes or other dissolved materials exceeds certain limits. Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose has a higher tolerance for salts in solution than methyl cellulose. Both are stable over a pH range of 3 to 11. Commercial water-soluble methyl cellulose products have a methoxy DS of 1.64 to 1.92. A DS of lower than 1.64 yields material with lower water solubility.The methoxy DS in hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose ranges from 1.3 to 2. Thehydroxypropyl MS ranges from 0.13 to 0.82. Methyl cellulose and hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose polymers have a number of applications and are used as thickeners in latex paints,food products,shampoos,creams and lotions, and cleansing gels. U.S.Patent 5,565,421 is an example of the use of hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose polymer to gel a light-duty liquid detergent containing anionic surfactants.
Identification test
It is soluble in water swelling, forming a transparent milky white sticky gel solution, and insoluble in ethanol.
Toxicity
ADI does not make special provisions (FAO/WHO, 2001).
It can be used for food safety (FDA. §172.87, 2000).
LD505200mg/kg (rats, intra peritoneal injection).
Limited use
FAO/WHO (1984): Cold drink ,10g/kg (in the end product design, single use or with other emulsifier, stabilizer and thickener dosage).
GB 2760-96: all kinds of food, to GMP limited.
Methods of production
Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose is obtained by treatment of fibrous plant material with alkali, methyl chloride and propylene oxide.1.The refined cotton cellulose with alkali treatment at 35-40 ℃ for half an hour, press, crushed the cellulose, aging at 35 ℃, so that the average degree of polymerization of alkali cellulose is in a desired range. The alkali fiber into etherification reactor, followed by adding epoxy propane and methane chloride, etherification at 50-80 ℃ for 5h, the maximum pressure is about 1.8MPa. The reaction products were produced by postprocessing (hydrochloric acid and oxalic acid, washing and drying). The consumption of raw material of cotton pulp 1100kg/t, methyl chloride and propylene oxide 4300kg/t, solid alkali 1200kg/t, hydrochloride 30kg/t, oxalic acid 50kg/t.2.100 kg refined cotton linters immersed in 45% solution, temperature is 35 to 40℃, time is 0.5 to 1 h, and then remove the press. The pressure to weight is 2.7 times as the weight of lint, stop pressure. Carry out the crushing. At 35℃, aging for 16h.In the reaction kettle, the chlorinated methane, propylene oxide were added into the reaction kettle. At 80℃, the pressure was 1.8 MPa, the reaction time is 5 to 8 h, and the amount of hydrochloric acid and oxalic acid were added to the hot water at 90℃. Dewatering with centrifuge, washing to neutral, when the water content of the material is below to 60% , 130℃ of hot air flow dried to the moisture content is below 5%. Finally, the finished product sieved by 20 mesh.3. Prepared by cellulose, methyl chloride, and ethylene oxide.
Production Methods
A purified form of cellulose, obtained from cotton linters or wood
pulp, is reacted with sodium hydroxide solution to produce a
swollen alkali cellulose that is chemically more reactive than
untreated cellulose. The alkali cellulose is then treated with
chloromethane and propylene oxide to produce methyl hydroxypropyl
ethers of cellulose. The fibrous reaction product is then
purified and ground to a fine, uniform powder or granules.
Hypromellose can then be exposed to anhydrous hydrogen chloride
to induce depolymerization, thus producing low viscosity grades.
Indications
Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose belongs to the group of medicines known as artificial tears. It is used to relieve dryness and irritation caused by reduced tear flow. It helps prevent damage to the eye in certain eye diseases. Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose may also be used to moisten hard contact lenses and artificial eyes. In addition, it may be used in certain eye examinations.
Side effects
Even though it may be rare, some people may have very bad and sometimes deadly side effects when taking a drug.Major & minor side effects for Hydroxypropyl MethylcelluloseBlurred visionDecrease/loss of visionEye painExcessive tearing of the eyeRedness in and around the eyes
Safety
Hypromellose is widely used as an excipient in oral, opthalmic,
nasal, and topical pharmaceutical formulations. It is also used
extensively in cosmetics and food products.
Hypromellose is generally regarded as a nontoxic and nonirritating
material, although excessive oral consumption may have a
laxative effect. The WHO has not specified an acceptable daily
intake for hypromellose since the levels consumed were not
considered to represent a hazard to health. In fact, high dosages
of hypromellose are being investigated for treating various
metabolic syndromes.
LD50 (mouse, IP): 5 g/kg(20)
LD50 (rat, IP): 5.2 g/kg
storage
Hypromellose powder is a stable material, although it is hygroscopic
after drying.
Solutions are stable at pH 3–11. Hypromellose undergoes a
reversible sol–gel transformation upon heating and cooling,
respectively. The gelation temperature is 50–90°C, depending
upon the grade and concentration of material. For temperatures
below the gelation temperature, viscosity of the solution decreases
as temperature is increased. Beyond the gelation temperature,
viscosity increases as temperature is increased.
Aqueous solutions are comparatively enzyme-resistant, providing
good viscosity stability during long-term storage. However,
aqueous solutions are liable to microbial spoilage and should be
preserved with an antimicrobial preservative: when hypromellose is
used as a viscosity-increasing agent in ophthalmic solutions,
benzalkonium chloride is commonly used as the preservative.
Aqueous solutions may also be sterilized by autoclaving; the
coagulated polymer must be redispersed on cooling by shaking.
Hypromellose powder should be stored in a well-closed
container, in a cool, dry place.
Incompatibilities
Hypromellose is incompatible with some oxidizing agents. Since it is
nonionic, hypromellose will not complex with metallic salts or ionic
organics to form insoluble precipitates.
Regulatory Status
GRAS listed. Accepted for use as a food additive in Europe.
Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (ophthalmic and
nasal preparations; oral capsules, suspensions, syrups, and tablets;topical and vaginal preparations). Included in nonparenteral
medicines licensed in the UK. Included in the Canadian List of
Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients.
Check Digit Verification of cas no
The CAS Registry Mumber 9004-65-3 includes 7 digits separated into 3 groups by hyphens. The first part of the number,starting from the left, has 4 digits, 9,0,0 and 4 respectively; the second part has 2 digits, 6 and 5 respectively.
Calculate Digit Verification of CAS Registry Number 9004-65:
(6*9)+(5*0)+(4*0)+(3*4)+(2*6)+(1*5)=83
83 % 10 = 3
So 9004-65-3 is a valid CAS Registry Number.
InChI:InChI=1/C36H70O19.C20H38O11/c1-19(37)9-45-17-27-29(47-11-21(3)39)31(48-12-22(4)40)34(51-15-25(7)43)36(54-27)55-30-28(18-46-10-20(2)38)53-35(52-16-26(8)44)33(50-14-24(6)42)32(30)49-13-23(5)41;1-21-9-11-13(23-3)15(24-4)18(27-7)20(30-11)31-14-12(10-22-2)29-19(28-8)17(26-6)16(14)25-5/h19-44H,9-18H2,1-8H3;11-20H,9-10H2,1-8H3/t19?,20?,21?,22?,23?,24?,25?,26?,27-,28-,29-,30-,31+,32+,33-,34-,35-,36+;11-,12-,13-,14-,15+,16+,17-,18-,19-,20+/m11/s1