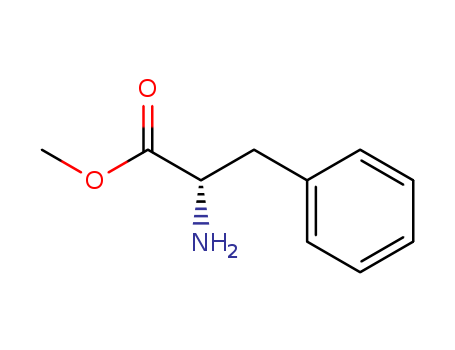
- Chemical Name:Methyl l-phenylalaninate
- CAS No.:2577-90-4
- Molecular Formula:C10H13NO2
- Molecular Weight:179.219
- Hs Code.:
- European Community (EC) Number:219-934-7
- UNII:10AT497I17
- Nikkaji Number:J31.465J
- Wikidata:Q27095740
- Metabolomics Workbench ID:150027
- ChEMBL ID:CHEMBL51969
- Mol file:2577-90-4.mol
Synonyms:(2S,3R)-(2-2H,3-2H)-phenylalanine methyl ester;L-phenylalanyl methyl ester;methyl phenylalanine;phenylalanine methyl ester;phenylalanine methyl ester, (D)-isomer;phenylalanine methyl ester, (DL)-isomer;phenylalanine methyl ester, hydrochloride, (D)-isomer;phenylalanine methyl ester, hydrochloride, (L)-isomer