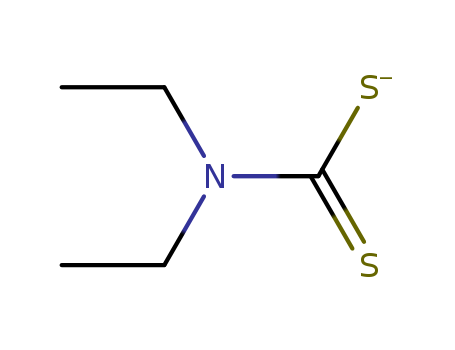
- Chemical Name:Diethyldithiocarbamate
- CAS No.:392-74-5
- Molecular Formula:C5H10NS2-
- Molecular Weight:148.273
- Hs Code.:
- DSSTox Substance ID:DTXSID90192448
- Nikkaji Number:J231.770B
- Wikidata:Q83065129
- Mol file:392-74-5.mol
Synonyms:Ammonium Salt Ditiocarb;Bismuth Salt Ditiocarb;Diethylcarbamodithioic Acid;Diethyldithiocarbamate;Diethyldithiocarbamate, Sodium;Diethyldithiocarbamate, Zinc;Diethyldithiocarbamic Acid;Dithiocarb;Ditiocarb;Ditiocarb Sodium;Ditiocarb, Ammonium Salt;Ditiocarb, Bismuth Salt;Ditiocarb, Lead Salt;Ditiocarb, Potassium Salt;Ditiocarb, Sodium Salt;Ditiocarb, Sodium Salt, Trihydrate;Ditiocarb, Tin(4+) Salt;Ditiocarb, Zinc Salt;Imuthiol;Lead Salt Ditiocarb;Potassium Salt Ditiocarb;Sodium Diethyldithiocarbamate;Sodium Salt Ditiocarb;Sodium, Ditiocarb;Thiocarb;Zinc Diethyldithiocarbamate;Zinc Salt Ditiocarb