10.1016/j.saa.2004.08.028
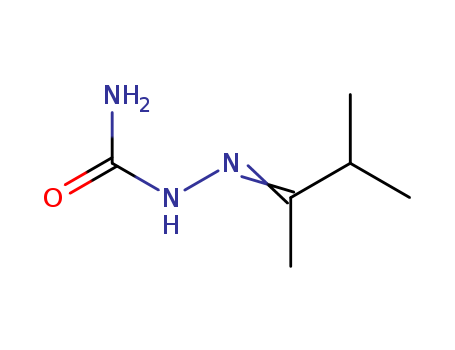
The research aims to synthesize and characterize manganese(II) complexes with ligands derived from semicarbazones and thiosemicarbazones. The study investigates the magnetic, electronic, and structural properties of these complexes to understand their potential applications in catalysis and biological systems. The key chemicals used include isopropyl methyl ketone semicarbazone (LLA), isopropyl methyl ketone thiosemicarbazone (LLB), 4-aminoacetophenone semicarbazone (LLC), and 4-aminoacetophenone thiosemicarbazone (LLD), which act as ligands, and manganese(II) salts such as MnCl2 and MnSO4. Isopropyl methyl ketone semicarbazone (LLA) plays a crucial role as one of the ligands used to form manganese(II) complexes. Specifically, LLA is used to create the complex [Mn(LLA)2Cl2], which is one of the primary subjects of the study. The purpose of using LLA is to investigate its coordination behavior with manganese(II) ions and to understand the resulting structural and electronic properties of the complex. The complexes were characterized using various spectroscopic techniques, including elemental analysis, molar conductance, magnetic susceptibility, EI-mass spectrometry, 1H NMR, IR, EPR, and electronic spectroscopy. The results showed that all complexes exhibit magnetic moments corresponding to five unpaired electrons, indicating a high-spin configuration. The geometries of the complexes were assigned based on spectral data, suggesting octahedral coordination for chloride complexes and tetrahedral coordination for sulfate complexes.