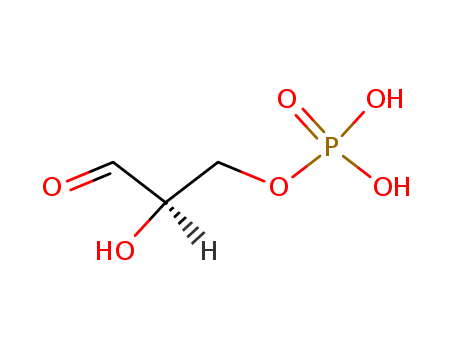
- Chemical Name:Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
- CAS No.:591-57-1
- Molecular Formula:C3H7O6P
- Molecular Weight:170.059
- Hs Code.:
- UNII:TD9ZNF8JPW
- DSSTox Substance ID:DTXSID70331398
- Nikkaji Number:J40.062I
- Wikidata:Q26992303
- Metabolomics Workbench ID:51939
- ChEMBL ID:CHEMBL1232918
- Mol file:591-57-1.mol
Synonyms:d-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate;591-57-1;glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate;Triose phosphate;D-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate;propanal, 2-hydroxy-3-(phosphonooxy)-, (2R)-;glyceraldehyde-P;TD9ZNF8JPW;[(2R)-2-hydroxy-3-oxopropyl] dihydrogen phosphate;3-Phosphoglyceraldehyde, D-;(2R)-2-Hydroxy-3-(phosphonooxy)-propanal;3-Phosphoglyceraldehyde, (+)-;CHEMBL1232918;CHEBI:29052;glyceraldehyde-3-P;2-Hydroxy-3-(phosphonooxy)propanal, (2R)-;(R)-2-Hydroxy-3-oxopropyl dihydrogen phosphate;D-glyceraldehyde-3-P;(2R)-2-hydroxy-3-oxopropyl dihydrogen phosphate;glyceraldehyde-phosphate;G3H;starbld0026332;UNII-TD9ZNF8JPW;SCHEMBL328992;DTXSID70331398;D-Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphoric acid;2-hydroxy-3-(phosphonooxy)-Propanal;BDBM50420199;DB02263;(2R)-2-Hydroxy-3-phosphonooxypropanal;HY-151223;CS-0609900;C00118;Propanal, 2-hydroxy-3-(phosphonooxy)-, (R)-;Glyceraldehyde, 3-(dihydrogen phosphate), D- (8CI);Q26992303;7086010C-A8E3-4CE8-92B2-FEB71ABE0B99