10.1016/0040-4020(77)80182-8
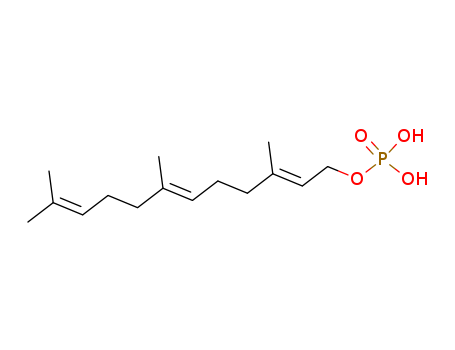
The research investigates the mechanism of the acid-catalyzed decomposition of farnesyl phosphates, aiming to determine whether the ionization of (Z,E)-farnesyl phosphate involves intramolecular assistance from the C-6/C-7 double bond or occurs via an unassisted process. The study examines the rates and products of the decomposition of various farnesyl phosphates, including (Z,E)- and (E,E)-farnesyl phosphate, their deuterated analogs, and t-butyl phosphate. The key chemicals used are farnesyl phosphates synthesized through different methods, formic acid for formolysis, various buffers for hydrolysis, and tetramethylammonium hydroxide for preparing phosphate solutions. The researchers measured the dissociation constants of the farnesyl phosphates and the rates of their acid-catalyzed decomposition. They also analyzed the product compositions and observed secondary deuterium kinetic isotope effects. The results show that while there is some evidence supporting both possibilities, the isotope data suggest that the ionization involves little to no assistance from the double bond, leading to the conclusion that the reaction is best viewed as an essentially unassisted process.