10.1080/15257770500544545
The research focuses on the microwave-assisted organic synthesis (MAOS) of 3-(D-gluco-pentitol-1-yl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole, a compound of interest in medicinal chemistry due to its pharmacological activities. The study aims to accelerate the synthesis of seco C-nucleosides of 1,2,4-triazole using microwave irradiation, which is reported to provide higher yields and purities compared to traditional synthetic methods. The chemicals used in the process include D-glucono- and D-galactono-1,5-lactones, thiocarbohydrazide, p-nitrobenzaldehyde, ethyl chloroacetate, and various reagents for subsequent reactions such as acetic anhydride, sodium acetate, and ammonium hydroxide. The conclusions of the research indicate that microwave irradiation significantly accelerates the synthesis of the target compounds, improving yields and reducing reaction times, thus demonstrating the effectiveness of MAOS in the synthesis of these potentially medicinally important compounds.
10.1007/BF00765589
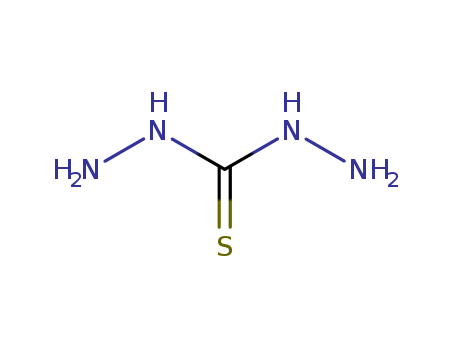
The research focuses on the synthesis and study of biological properties of certain chemical compounds. One part of the research involves the synthesis and pharmacological investigation of analogs of sydnocarb and inkasan. The compounds synthesized include those with hydrophobic and hydrophilic properties, and their central stimulant activity is studied. The chemicals involved in this part of the research include sydnocarb, compounds (I, II, III), N,N-dialkylaminoethyl substituted β-carbolines (IIa, b), azepino[3,4-b]indole (V), and dichlorophosphonates (VI). Another part of the research involves the synthesis of new derivatives of 5-carboxymethylthiazolidine-2,4-dione and thiocarbohydrazide. The main starting materials for this synthesis are thiosemicarbazones of 4-alkoxybenzaldehydes and 4-alkoxyacetophenones. The chemicals involved in this part of the research include maleic anhydride, thiosemicarbazide, and thiocarbohydrazide.
10.1080/10426500802625594
The research aimed to synthesize new heterocyclic Schiff bases derived from 2-amino-3-formylchromone and investigate their antimicrobial activity. The study focused on combining chromone moieties with 1,2,4-triazole or 1,2,4-triazine derivatives through an azomethine linkage to create novel nitrogen heterocyclic systems. Key chemicals used included 2-amino-3-formylchromone as the starting material, various hydrazine derivatives (such as benzoylhydrazine, cyanoacetohydrazide, and thiocarbohydrazide) for condensation reactions, and electrophilic reagents like benzoyl chloride, acetic anhydride, and carbon disulfide for further heterocyclization. The newly synthesized compounds were characterized using IR, 1H NMR, and mass spectrometry. The antimicrobial activity of these compounds was tested against a range of bacteria and fungi, revealing that compounds 8 and 20 showed moderate activity against bacteria and high activity against fungi, while compounds 9, 13, and 15 exhibited high antifungal activity. The study concluded that the synthesized compounds have potential as antimicrobial agents, particularly those incorporating dithioxo-1,2,4-triazole and antipyrine moieties, and suggested that further modifications could enhance their biological efficacy.
10.1002/ardp.19913240605
The study investigates the reaction between isatin and thiocarbohydrazide, aiming to clarify the structure of the resulting compound. Isatin, a versatile intermediate in heterocyclic chemistry, and thiocarbohydrazide, a thiosemicarbazide derivative, are the primary chemicals involved. The authors challenge the previously reported structure of the reaction product as a spiro system (2-oxo-1',2',4',5'-tetrahydro-spiro[3H-indole-3,3'-1,2,4,5-tetrazine]-6'-thione) and propose that the actual product is a thiocarbohydrazone. They support their claim through various experiments, including condensation reactions with benzaldehyde and α-keto acids, which yield different derivatives. The study also examines the biological activity of these compounds against various strains of bacteria, yeast, and fungi, revealing varying levels of sensitivity. The findings highlight the importance of additional spectral and chemical evidence in determining the structure of complex organic compounds and underscore the potential biological applications of these derivatives.


 T+
T+


