10.1248/cpb.39.515
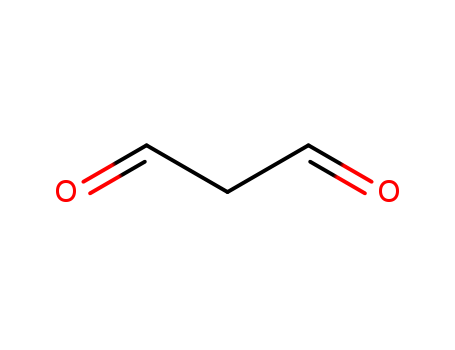
The study investigates the reaction of malonaldehyde with nucleic acids, specifically focusing on the formation of pyrimido[1,2-a]purin-10(3H)-one nucleoside (3) through the thermal decomposition of diastereomers containing oxadiazabicyclononene residues linked to guanosine. Malonaldehyde, a product of lipid peroxidation and prostaglandin biosynthesis, is known for its mutagenic and carcinogenic properties. In this research, guanosine reacts with 1,1,3,3-tetraethoxypropane, which acts as a generator of malonaldehyde, under strongly acidic conditions to form diastereomers 4a and 4b. These diastereomers are then decomposed by heat, yielding the desired pyrimido[1,2-a]purin-10(3H)-one nucleoside (3) in a good yield. The study also proposes a convenient method for the preparation of compound 3, which includes the thermal decomposition process of the diastereomers. The findings suggest that this method is rapid and effective, significantly improving the yield of compound 3 compared to previous methods.