10.1002/ejoc.201501084
The study investigates the use of a sterically congested α-cyanoamine as an effective cyanating reagent for the cyanation of acetals and orthoesters. The key chemicals used in the study include α-cyanoamines, which were prepared from secondary amines and α-bromoacetonitrile, and trichlorosilyl triflate (SiCl3OTf), which acts as a catalyst. These chemicals serve the purpose of facilitating the cyanation reaction, leading to the production of cyanated adducts in high yields. The α-cyanoamines were found to be influenced by steric effects, with more hindered amines improving the product yield, suggesting that they prevent the formation of unfavorable complexes with the catalyst and retain their cyanating functionality. The study also detected oxocarbenium cations as intermediates through NMR spectroscopy, providing insights into the reaction mechanism.

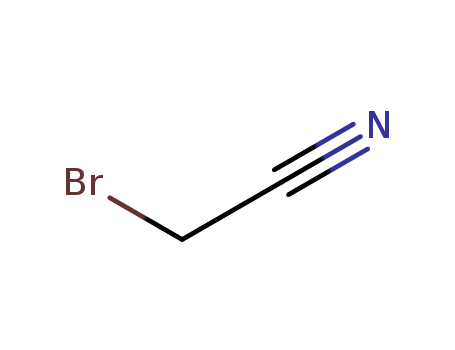

 T,
T,  C
C


