10.1055/s-2006-957878
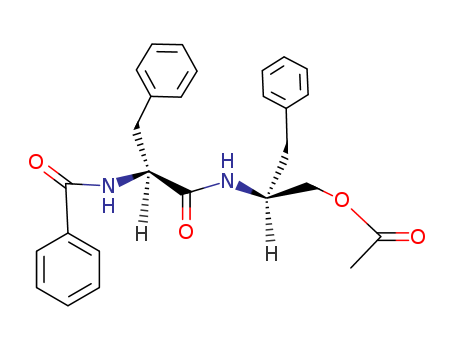
The research focuses on the isolation and synthesis of aurantiamide acetate, a compound with potential anticancer properties, from the plant Arisaema erubescens, which is traditionally used in Chinese medicine. The purpose of the study was to identify the active agents responsible for the plant's anticancer effects. Through chromatographic separation of a methanol extract, aurantiamide acetate was isolated and its structure was confirmed by synthesis. The chemicals used in the process included methanol for extraction, hexane and chloroform for partitioning, and ethyl acetate as an eluent in chromatography. The conclusions of the research were that aurantiamide acetate was successfully isolated and synthesized, and its structure was confirmed by matching the NMR spectra of the synthetic product with that isolated from A. erubescens. Additionally, aurantiamide acetate was found to be non-toxic to K562 human leukemia cells, suggesting its potential as a safe anticancer agent.