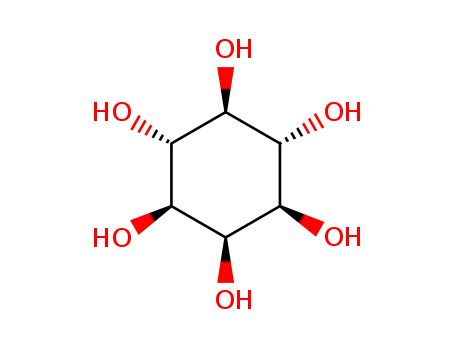
- Chemical Name:Inositol
- CAS No.:87-89-8
- Deprecated CAS:53319-35-0,887751-76-0,36190-90-6,19030-27-4,173524-45-3
- Molecular Formula:C6H12O6
- Molecular Weight:180.158
- Hs Code.:2906.13
- European Community (EC) Number:201-781-2,211-394-0,230-024-9,207-682-0,207-681-5,209-000-7,211-393-5,610-437-4
- NSC Number:757076,404118,127230,103959,55558,55552,55551,45517,25142,8101
- UNII:8LQ63P85IC,63GQX5QW03,9O6Y5O4P9W,M94176HJ2F,R1Y9F3N15A,6R79WV4R10,1VS4X81277,4L6452S749,4661D3JP8D,587A93P465
- DSSTox Substance ID:DTXSID7023146,DTXSID30110000,DTXSID101028818,DTXSID101028820,DTXSID201028823,DTXSID301028826,DTXSID50905091,DTXSID601028825,DTXSID901028824
- Nikkaji Number:J4.282J,J522.945F,J9.771C,J92.778C,J101.888D,J101.889B,J101.890F,J101.891D,J101.892B
- Wikipedia:Inositol,Allo-Inositol,1D-chiro-Inositol,Scyllo-Inositol,Neo-Inositol,Muco-Inositol,1L-chiro-Inositol,Epi-Inositol,Cis-Inositol
- Wikidata:Q407997,Q2838375,Q3011024,Q743661,Q3023527,Q3205874,Q3347078,Q3331426,Q3589114,Q2974313
- NCI Thesaurus Code:C122987,C28163,C189814
- RXCUI:5833
- Metabolomics Workbench ID:49811
- ChEMBL ID:CHEMBL468154,CHEMBL1950780,CHEMBL1231671,CHEMBL1222251,CHEMBL278373,CHEMBL3976780
- Mol file:87-89-8.mol
Synonyms:inositol;myo-inositol;Scyllo-inositol;epi-Inositol;Muco-Inositol;Allo-inositol;i-Inositol;87-89-8;meso-Inositol;Neo-inositol;1D-Chiro-inositol;1L-Chiro-inositol;D-(+)-chiro-Inositol;cis-Inositol;643-12-9;488-59-5;D-chiro-Inositol;Myoinositol;Scyllitol;6917-35-7;Cyclohexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexaol;488-58-4;cyclohexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexol;Quercinitol;mesoinositol;Cocositol;551-72-4;Meat sugar;Myoinosite;Dambose;chiro-inositol;Inositene;Inositina;L-chiro-Inositol;Phaseomannite;Inosital;Inosite;Iso-inositol;Cyclohexitol;Phaseomannitol;41546-34-3;Inositol, myo-;Mesoinosit;Mesoinosite;Scyllite;Mesovit;Nucite;Mesol;643-10-7;488-55-1;Cyclohexanehexol;Inositol, meso-;cis-1,2,3,5-trans-4,6-Cyclohexanehexol;D-myo-Inositol;D-chiro Inositol;488-54-0;Bios I;Insitolum;Isoinositol;L-(-)-chiro-Inositol;(-)-Inositol;576-63-6;d-Inositol;L-Inositol;L-myo-Inositol;Inositol, allo-;Inositol, muco-;Inositol, i-;Inositol, scyllo-;Inositol (VAN);alloinositol;neoinositol;Hexahydroxycyclohexane;scyllo-Cyclohexanehexol;1D-myo-Inositol;1L-myo-Inositol;Inositol, cis-;Inositol, epi-;Inositol, neo-;epi-Cyclohexanehexol;(+)-Inositol;1,2,3,4,5,6-Cyclohexanehexol;(-)-chiro-Inositol;ELND005;Rat antispectacled eye factor;Levoinositol;CCRIS 6745;1,2,3,5-trans-4,6-Cyclohexanehexol, cis-;Mouse antialopecia factor;AZD 103;Chiro-inositol, (-)-;Inositol, myo;(1R,2R,3S,4R,5r,6S)-cyclohexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexaol;38876-99-2;MFCD00077932;(1r,2r,3r,4r,5r,6r)-cyclohexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexol;1,3,5/2,4,6-Hexahydroxycyclohexane;(1R,2R,3R,4R,5S,6S)-Cyclohexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexaol;(1R,2R,3S,4S,5S,6S)-Cyclohexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexaol;1-L-chiro-Inositol;Inositol, D-chiro-;ELND 005;(+)-Chiro-Inositol;CHEBI:17268;AI3-16111;NSC8101;1,3,5/2,4,6-cyclohexanehexol;1,2,3,5/4,6-Cyclohexanehexol;NSC 8101;NSC-8101;Chiro-inositol, (+)-;(1r,2R,3S,4r,5R,6S)-cyclohexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexol;EINECS 201-781-2;(1R,2R,3R,4S,5S,6s)-cyclohexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexaol;(1R,2R,3S,4S,5S,6S)-cyclohexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexol;1,2,3,4,5,6-HEXAHYDROXY-CYCLOHEXANE;NSC-25142;NSC-55551;NSC404118;myo-Inositol;NSC 404118;NSC-404118;UNII-63GQX5QW03;UNII-8LQ63P85IC;UNII-9O6Y5O4P9W;UNII-R1Y9F3N15A;Inositol [Nonspecific isomer];UNII-4661D3JP8D;UNII-6R79WV4R10;UNII-M94176HJ2F;J101.890F;J101.891D;(1s,2s,3s,4s,5s,6s)-cyclohexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexol;63GQX5QW03;8LQ63P85IC;9O6Y5O4P9W;ELND-005;R1Y9F3N15A;(1R,2R,3R,4R,5S,6S)-cyclohexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexol;(1r,2R,3R,4s,5S,6S)-cyclohexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexol;(1s,2R,3R,4s,5S,6S)-cyclohexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexol;DTXSID7023146;UNII-1VS4X81277;CHEBI:10642;CHEBI:23927;CHEBI:27372;CHEBI:27987;AZD-103;4661D3JP8D;6R79WV4R10;M94176HJ2F;UNII-4L6452S749;UNII-587A93P465;Inositol (NF);Inositol (VAN8C;Inositol [NF];NSC45517;NSC55551;NSC55552;EINECS 207-681-5;EINECS 207-682-0;EINECS 209-000-7;EINECS 211-393-5;EINECS 211-394-0;EINECS 230-024-9;NSC 25142;NSC-55552;NSC-55558;1VS4X81277;NSC-103959;NSC-127230;INS;NCGC00159409-02;(1R,2R,3S,4R,5S,6S)-cyclohexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexaol;(1R,2R,3S,4R,5S,6S)-cyclohexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexol;(1r,2R,3S,4s,5R,6S)-cyclohexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexol;4L6452S749;587A93P465;Inositol, myo- (8CI);MYO-INOSITOL-1,2,3,4,5,6-D6;1,3,4,5,6-Cyclohexanehexol;1,3,5/4,6-Cyclohexanehexol;DTXCID2065254;1,2,4/3,5,6-cyclohexanehexol;rel-(1r,2r,3r,4r,5r,6r)-Cyclohexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexaol;rel-(1R,2r,3S,4R,5s,6S)-Cyclohexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexaol;1,2,3,4,5,6-Cyclohexanehexol #;cis-1,2,3,4,5,6-cyclohexanehexol;CAS-87-89-8;cis-1,3,5-trans-4,6-Cyclohexanehexol;SMR000857145;SMR000857319;SMR000857320;Inositol NF 12;SR-05000001655;MFCD00065455;1,2,3,4,5,6-Hexahydroxycyclohexane;inositols;an inositol;Mio-inositol;Muscle sugar;inositol myo-;Myo- inositol;Inositol FCC;4irx;Inositol, chiro-;rac-chiro-inositol;Inosital (TN);CBU;EPIINOSITOL;(+)-Epi-Inositol;CHIRO-INOSITOLS;Epi-inositol, 98%;allo-Inositol, 97%;Inositol [USAN:NF];INOSITOL, MESO;Spectrum_001595;2os9;INOSITOL [INCI];INOSITOL [USAN];D-( )-chiro-Inositol;INOSITOL [FCC];INOSITOL [INN];orthorhombic myo-inositol;D-(+)-Chiro Inositol;DL-CHIRO-INOSITOL;INOSITOL [MI];INOSITOL (D);INOSITOL (L);INOSITOL [VANDF];Spectrum3_001053;Spectrum4_001193;Spectrum5_000961;myo-Inositol, >=99%;INOSITOL [MART.];bmse000102;bmse000103;bmse000113;bmse000901;bmse000922;D03SHD;D07CPO;D08DXZ;D0B1EY;D0Y4UQ;Epitope ID:144993;INOSITOL [USP-RS];INOSITOL [WHO-DD];scyllo-Inositol, >=98%;SCHEMBL5831;SCHEMBL5832;SCHEMBL5969;NCIOpen2_008191;BSPBio_002606;KBioGR_001885;KBioSS_002075;MLS001332377;MLS001332378;MLS001335965;MLS001335966;MLS001335967;MLS001335968;SCHEMBL187278;SCHEMBL187397;SCHEMBL187796;SCHEMBL188106;SCHEMBL188237;SCHEMBL491333;SCHEMBL959404;SCHEMBL959405;CHEMBL278373;CHEMBL468154;GTPL4495;GTPL4645;GTPL4648;GTPL4649;MEGxp0_001817;SCHEMBL1055883;SCHEMBL4748543;SCHEMBL6378921;SCHEMBL6468882;SCHEMBL6791918;CHEMBL1222251;CHEMBL1231671;CHEMBL1950780;CHEMBL3976780;SCHEMBL12371461;SCHEMBL12377889;SCHEMBL12411898;SCHEMBL12711208;SCHEMBL12735687;SCHEMBL13058696;SCHEMBL13114115;SCHEMBL13114116;SCHEMBL13114128;SCHEMBL13207905;SCHEMBL13580047;SCHEMBL14542470;SCHEMBL21388397;ACon1_002457;CHEBI:22357;CHEBI:23311;CHEBI:24848;CHEBI:25492;CHEBI:27374;D-(+)-chiro-Inositol, 95%;KBio2_002075;KBio2_004643;KBio2_007211;KBio3_001826;L-(-)-chiro-Inositol, 95%;AXD 103;DTXSID30110000;DTXSID50905091;myo-Inositol, p.a., 98.0%;1,2,3,4,5/6-cyclohexanehexol;1,2,3,4/5,6-cyclohexanehexol;1,2,3/4,5,6-cyclohexanehexol;1,2,4,5/3,6-cyclohexanehexol;DTXSID101028818;DTXSID101028820;DTXSID201028823;DTXSID301028826;DTXSID601028825;DTXSID901028824;HMS2091N13;HMS2230N03;HMS2235H05;HMS2235M23;HMS3369B06;HMS3369F20;HMS3373E05;Pharmakon1600-01500352;D-CHIRO-INOSITOL [USP-RS];D-CHIRO-INOSITOL [WHO-DD];1,2,3,4,5,6-Cyclohexanehexaol;BCP25172;HY-B1411;HY-N3021;MYO-INOSITOL [EP MONOGRAPH];NSC25142;NSC55558;D-myo-Inositol, Cell Culture Grade;Tox21_111642;Tox21_302035;CCG-36096;cis-Inositol, >=98.0% (TLC);MFCD00003863;MFCD00272608;MFCD00799555;MFCD00799556;MFCD01321249;NSC 55552;NSC 55558;NSC-45517;NSC103959;NSC127230;NSC757076;s4530;STL453612;epi-Inositol, >=98.0% (HPLC);1,2,3,4,5,6/0-cyclohexanetetrol;AKOS006240678;AKOS006332036;AKOS015895894;AKOS015912905;AKOS015912934;AKOS015960429;AKOS015960633;AKOS015994742;AKOS024318869;Tox21_111642_1;CS-4782;CS-W010757;CS-W017225;DB03106;DB13178;DB15350;HY-W010041;HY-W016509;HY-W021265;HY-W127726;J9.771C;KS-1284;KS-1420;LS-2350;NSC 103959;NSC 127230;NSC-757076;SB44732;SB45039;SB46764;SB46855;D-chiro-Inositol, >=98.0% (HPLC);NCGC00159409-03;NCGC00159409-04;NCGC00169828-01;NCGC00178580-01;NCGC00178580-03;NCGC00255362-01;AC-11070;AS-10616;AS-68396;AS-68424;cyclohexane-1R,2R,3S,4S,5R,6S-hexol;NCI60_041778;SY060836;myo-Inositol, purum, >=98.0% (HPLC);rac-chiro-1,2,3,4,5,6-cyclohexanehexol;SBI-0051369.P003;cis-1,2,4-trans-3,5,6-Cyclohexanehexol;HY-121962;J101.888D;J101.889B;J101.892B;myo-Inositol, for microbiology, >=99.0%;CS-0023004;CS-0039882;CS-0083766;CS-0185922;CS-0369552;FT-0627237;FT-0632208;FT-0632209;FT-0632730;FT-0652045;FT-0670351;FT-0670357;FT-0693444;FT-0693614;I0040;I0628;I0629;I0630;I0631;I0632;I0633;S6176;EN300-82941;myo-Inositol, BioUltra, >=99.5% (HPLC);myo-Inositol, SAJ special grade, >=99.0%;myo-Inositol, Vetec(TM) reagent grade, 99%;C00137;C06151;C06152;C06153;C19891;D08079;D78450;D91187;D91188;D91189;E78671;EN300-658805;F19572;I-6500;M01914;T72516;AB00051982_13;EN300-7361851;EN300-7411506;A834712;A836375;A866896;EN300-19631206;EN300-19632288;EN300-25914216;Q407997;Q743661;Q-201583;Q2838375;Q2974313;Q3011024;Q3023527;Q3205874;Q3331426;Q3347078;Q3589114;SR-05000001655-1;SR-05000001655-5;W-202861;W-202862;W-203081;W-203168;W-203392;1,2,4/3,5,6-Cyclohexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexol;7B0CEF84-D9CE-4A88-AA7D-EC50C89387A5;1D7A27BF-6060-4FA9-AC46-3BD18DBA406E;220128F1-89BF-442D-AD6D-E6D1EA7BA625;Z1486007281;(1r,2r,3r,4r,5r,6r)-cyclohexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexaol;(1R,2S,3r,4R,5S,6r)-cyclohexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexol;(1R,2S,3r,4R,5S,6s)-cyclohexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexol;(1R,2S,3s,4R,5S,6s)-cyclohexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexol;Inositol, United States Pharmacopeia (USP) Reference Standard;myo-Inositol, European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard;(1R,2R,3S,4S,5S,6R)-CYCLOHEXANE-1,2,3,4,5,6-HEXOL;1,2,3,4,5,6-Cyclohexanehexol, (cis,cis,cis,trans,cis,trans)- #;1,2,3,4,5,6-cyclohexanehexol, (1alpha,2alpha,3alpha,4beta,5alpha,6beta);Inositol, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard;Certified Reference Material;1.ALPHA.,2.ALPHA.,3.BETA.,4.ALPHA.,5.BETA.,6.BETA.-CYCLOHEXANEHEXOL;173524-45-3;2H3;myo-Inositol, BioReagent, suitable for cell culture, suitable for insect cell culture, suitable for plant cell culture