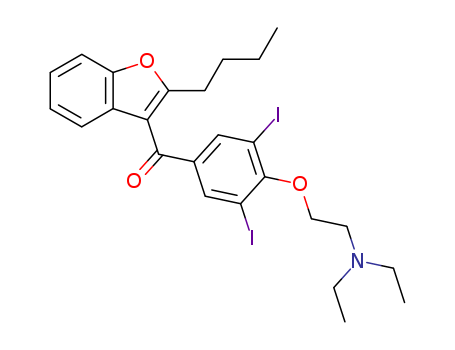
- Chemical Name:Amiodarone
- CAS No.:1951-25-3
- Molecular Formula:C25H29I2NO3
- Molecular Weight:645.319
- Hs Code.:2932999099
- European Community (EC) Number:217-772-1
- UNII:N3RQ532IUT
- DSSTox Substance ID:DTXSID7022592
- Nikkaji Number:J7.829H
- Wikipedia:Amiodarone
- Wikidata:Q410061
- NCI Thesaurus Code:C62002
- RXCUI:703
- Pharos Ligand ID:87DVJ1X9QF62
- Metabolomics Workbench ID:43343
- ChEMBL ID:CHEMBL633
- Mol file:1951-25-3.mol
Synonyms:Amiobeta;Amiodarex;Amiodarona;Amiodarone;Amiodarone Hydrochloride;Amiohexal;Aratac;Braxan;Corbionax;Cordarex;Cordarone;Hydrochloride, Amiodarone;Kordaron;L 3428;L-3428;L3428;Ortacrone;Rytmarone;SKF 33134 A;SKF 33134-A;SKF 33134A;Tachydaron;Trangorex


 Xn
Xn


