10.1007/BF00484356
The research focuses on the development of synthetic methods for alkane and cyclohexane derivatives featuring two heterocyclic substituents from the furan, pyrrole, and thiophene series. These compounds, which contain two five-membered aromatic heterorings with one heteroatom, are prevalent in natural compounds but have not been extensively synthesized. The study explores the electrophilic addition of monocarboxylic acid chlorides and dicarboxylic acid dichlorides to allyl or methallyl chlorides, leading to the synthesis of bisfuran, bispyrrole, and bisthiophene derivatives. Key chemicals used in the process include adipic and cyclohexane-1,4-dicarboxylic acid dichlorides, allyl or methallyl chlorides, aluminum chloride, primary amines, phosphorus pentasulfide, and ethylenediamine. The conclusions of the research highlight the successful development of simple and convenient preparative methods for synthesizing a range of these heterocyclic derivatives, which were confirmed through spectral data and chemical transformations.
10.1016/S0040-4020(01)96070-3
The research describes the successful total synthesis of the dimeric alkaloid amauromine, a compound of interest due to its unique structure and biological activity as a vasodilator. The purpose of the study was to achieve the first total synthesis of amauromine using a convergent synthetic route based on the thio-Claisen rearrangement reaction through a sulphonium salt, starting from L-tryptophan. Key chemicals used in the synthesis include L-tryptophan, phosphorus pentasulfide, methyl iodide, dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC), N-hydroxysuccinimide (HOSu), potassium carbonate, prenyl bromide, titanium tetrachloride, and lithium aluminium hydride. The synthesis involved multiple steps, including oxidation, esterification, introduction of methylthio function, formation of the key intermediate diketopiperazine, thio-Claisen rearrangement, catalytic reduction, and reductive desulphurization. The final step involved concurrent cyclization and reductive desulphurization using TiCl4-LiAlH4 to obtain amauromine. The study concluded that the total synthesis was achieved with a yield of 15%, and the synthesized amauromine was identical to the natural compound in all respects, confirming the success of the synthetic route. This achievement supports the hypothesis on the mode of introduction of the inverted isoprene unit in related indole alkaloids and provides a potential pathway for the biosynthesis of amauromine.
10.1002/jhet.4167
The study focuses on the synthesis, characterization, and evaluation of novel 1,5-benzodiazepine derivatives (compounds 2-7) for their potential applications in corrosion inhibition and antibacterial activities. The chemicals used in the study include 1-ethyl-4-phenyl-1,5-benzodiazepine-2-thione, phosphorus pentasulfide, hydrazine hydrate, carbon disulfide, and various alkylating agents such as propargyl bromide, benzyl chloride, and ethyl bromoacetate. These chemicals served the purpose of synthesizing the target benzodiazepine derivatives through a series of reactions including sulfurization, condensation, and alkylation. The synthesized compounds were then characterized using spectroscopic techniques and single-crystal X-ray crystallography. The study aimed to determine the molecular and crystal structures of these compounds, analyze their intermolecular interactions through Hirshfeld surface analysis, and evaluate their potential as corrosion inhibitors for aluminum, copper, and iron in acidic media using Monte Carlo simulations. Additionally, the antibacterial activity of these compounds against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria was assessed, with the results indicating their potential as antibacterial agents.
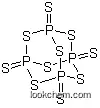


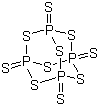
 F,
F, Xn,
Xn, N
N
