10.1021/jo801808r
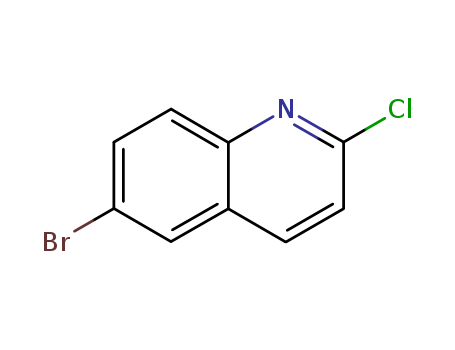
The research focuses on the development of new 6-heterocyclic substituted 2-aminoquinolines using Buchwald-Hartwig amination reactions. These compounds are designed to have increased binding affinity for the Tec Src Homology 3 (SH3) domain, a protein-protein interaction domain that is a valuable target for therapeutic agents. The study explores the selective amination of an aryl bromide in the presence of an activated heteroaryl chloride, optimizing reaction conditions to achieve cross-coupling with various cyclic amines. Key chemicals involved in the research include 6-bromo-2-chloroquinoline as the starting material, palladium catalysts such as Pd(OAc)2, various phosphine ligands like CataCXium A (16), and bases like KOtBu and NaOtBu. The reactions also utilize a range of cyclic amines as coupling partners to introduce different heterocyclic substituents at the 6-position of the quinoline ring. The study further investigates the use of lithium bis(trimethylsilyl)amide (LHMDS) as an ammonia equivalent for the amination process to convert 2-chloroquinolines to 2-aminoquinolines, providing an improved method over traditional approaches. The binding affinity of the synthesized compounds with the Tec SH3 domain is assessed through NMR chemical shift perturbation analysis, revealing that the new ligands exhibit enhanced binding affinities compared to the lead compound, 2-aminoquinoline.