327-97-9 Usage
Description
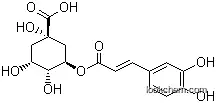
Chlorogenic acid, a bioactive polyphenolic compound, is predominantly found in plants such as coffee. It exhibits a range of beneficial properties, including being a potent neuroprotectant, antiviral, antifungal, antioxidant, and antitumor agent. Additionally, it plays a role in regulating glucose and lipid metabolism and improving insulin sensitivity.
Uses
Used in Pharmaceutical Applications:
Chlorogenic acid is used as a pharmaceutical raw material and intermediate due to its broad-spectrum antimicrobial properties, having an obvious inhibitory effect on hemolytic streptococcus, dysentery rod gas, and salmonella typhi bacteria. It also has antibacterial, antiviral, hemostatic, and white blood cell-increasing effects, with shortened blood clotting and bleeding times, making it useful in the treatment of upper respiratory tract infections, anti-inflammatory, and antipyretic applications.
Used in Antioxidant Applications:
Chlorogenic acid serves as an antioxidant and free radical scavenger, protecting against oxidative stress-induced conditions such as diabetes and potentially cardiovascular disease.
Used in Weight Loss Applications:
As a major component of green coffee extracts, chlorogenic acid promotes weight loss in overweight and obese individuals.
Used in Food Industry:
Chlorogenic acid is utilized as a food additive in coffee products, chewing gum, and mint, where it acts as an intermediate in the biosynthesis of lignin, an antioxidant.
Used in Industrial Applications:
Chlorogenic acid is an important intermediate in lignin biosynthesis, which has various industrial applications.
Pharmacological action
Chlorogenic acid is also called "green" auspicious acid, tannins "coffee", "coffee tannic acid", is a plant produce a styrene acrylic compounds through shikimic acid hitches in aerobic respiration process.It is coffee acyl quinic acid derivatives.The oxidation resistance is strong, and also has the anti HIV, anti tumor cells, antibacterial, improve central excited, cholagogue function.It has teratogenic, allergy and regulate the activity of cytochrome P450 ligase, and other functions.It is widely exist in more content honeysuckle plants. It is obtained by the water needle crystal, and it is the hemihydrate, when 110 ℃ it is to hydrate. Melting point is 208 ℃, [a] D25 33.5 ° (water, C = 1), K = 2.2 x 10-3 (27 ℃).It is weak acidity and convergence. When 25 ℃ , the solubility in water is 4%, easily soluble in hot water, but soluble in ethanol, acetone, slightly soluble in ethyl acetate, insoluble in chloroform, ether and carbon disulfide. It is azeotropic with concentrated hydrochloric acid and come to blue dye. It can make the bromine water fade, It is azeotropic with strong hydrogen iodide and obtain benzoic acid, It is obtained phenol by thermal decomposition together with water at 230 ℃, It decomposite to caffeic acid and quinic acid with dilute hydrochloric acid, and caffeic acid and quinic acid with dilute alkali at room temperature. Chlorogenic acid and its isomer different chlorogenic acid and green chlorogenic acid are in fruits of dicotyledonous plants, leaves, and other organizations,which is an important factor for plant metabolism. Chlorogenic acid has good biological activity, the transparent acid enzyme and inhibition of glucose-6-phosphatase, free radical lipid perxidation qing mutagenesis resistance and cardiovascular crown reinforcement, special efficacy in lipid-lowering, both anti-bacterial anti-virus, protecting liver cholagogic.
Chlorogenic acid as the condensation product of caffeic acid and quinic acid, is blue when meeting with iron, which is similar to tannins , but not precipitated with protein, so no convergence. Caffeic acid and chlorogenic acid has the wide bacteriostasis, but can be inactivated protein in the body. This product is similar to caffeine, oral or intraperitoneal injection, can improve the rat central excitability. Oral the drug of chlorogenic acid and coffee acid can increase the amount of hydrochloric acid secretion in the stomach, and can make slow pulse, and quinic acid is not. Chlorogenic acid could significantly increase small intestine peristalsis on the rat or mouse. Chlorogenic acid, caffeic acid and quinic acid can increase the tension of rat uterus, this function can be cancelled by papaverine, while atropine can't influence. Caffeic acid, chlorogenic acid, also can promote bile secretion in rats. On the specimens of rabbit ileum in vitro, this product can enhance the effect of adrenaline, but has no effect on blood glucose of adrenaline.
Protecting liver, gallbladder
Chlorogenic acid in flos lonicerae has favorable gallbladder function, promoting biliary Secretion of rats. Injection of 200 mg/kg chlorogenic acid to browns MAO honeysuckle total saponins subcutaneous can be significantly against CCl4, paracetamol and the increase of serum GPT caused by galactosamine in mice liver and liver triglyceride levels, and significantly reduce the severity of the liver pathological damage, making dot necrosis number sum and necrosis occur rate liver decreased obviously.
The inhibitory effect on hyaluronidase and glucose - 6 - phosphatase
Hyaluronic cranberry (HAase) is one of the cracking mucopolysaccharide enzymes, can catalyze hyaluronic acid (HA) decomposition,which is in relation to the permeability of vascular system and inflammation. HA is a mucopolysaccharide, which is composed of uronic acid and acetyl glucosamine, having a variety of functions, such as heal, make the skin wetting health, lubricating joints and prevent inflammation, etc. 3, 5-2 coffee acyl quinic acid (artichoke acid) and chlorogenic acid found in the ethyl acetate extract from the narrow assists cone flower (Echinacea amgustifolia DC) roots have stronger inhibitory effect of HAase activated.
Animal in vitro studies have demonstrated that chlorogenic acid can not reversible inhibition of glucose-6-hydrolysis of phosphatase, reduce liver glycogen decomposition and exogenous glucose absorption. Animal studies have shown that the use of chlorogenic acid can reduce high blood sugar spikes caused by the use of glucagon (glycogenolysis). Therefore, chlorogenic acid can lower blood sugar level, improve the liver glucose-6-phosphoric acid and the concentration of hepatic glycogen.
The character of molecular structure
Chlorogenic acid is formed by caffeic acid and quinic acid, and the molecular structure has ester bond, unsaturated double bond and polyphenol unstable part of the three. In the process of extracted from plants, chlorogenic acid often happen by hydrolysis and intramolecular ester base migration isomerization . Due to the special structure of chlorogenic acid, it can extract from plants by the polarity solvent such as ethanol, acetone, methanol. But due to the instability of chlorogenic acid itself, extraction can not be in high temperature, strong light and heat for a long time. Chlorogenic acid liquid were placed in brown bottle, refrigerator (2 ℃) to save to be the most stable.
Preparation method
It can be obtained by (1S)-1-ethoxyformyloxy-3-cis-[3,4-dihydroxy-anti-cinnamoyl oxygen radicals]-4'-anti-5'-anti-dihydroxy cyclohexane-γ-methyl formate with barium hydroxide in methanol catalytic hydrolysis, or by the segregation from green coffee beans.
HPLC method for determination the content
(1)Chromatographic conditions: octadecyl silane bonded silica gel as the filling agent; Acetonitrile-0.4% phosphoric acid solution (13:87) as mobile phase; Detection wavelength of 327 nm. Theoretical plate number according to the chromatographic peak of chlorogenic acid is greater than 1000.
(2)the preparation of the reference substance solution: precisely weigh the right amount of chlorogenic acid reference substance, placed in brown volumetric flask, adding 50% methanol solution containing 40 μg /mL (saving below 10 ℃).
(3)the preparation of sample solution: taking samples of dry powder is about 0.5 g, precision said, with a plug in the conical flask, adding 50 ml 50% methanol , 30 min ultrasonic processing , cooling, weighing, make up the weight loss reduction with 50% methanol, shake well, filtration, abandoned the early filtrate, precision measuring duration of filtrate 5 ml, 25 ml volumetric brown flask , add 50% methanol to the scale, shake well.
(4)assimilate precision respectively from each 10 μL reference substance and the sample solution, injection liquid chromatograph, determination,obtained.
Toxicity
Chlorogenic acid is sensitive to people, can cause asthma, dermatitis, but no this reaction to the oral of chlorogenic acid. It can be active no sensitization substances by small intestinal secretions convertion to. The toxicity of chlorogenic acid is very small, LD50 is greater than 1 g/kg to young rats, intraperitoneal injection of greater than 0.25 g/kg.
Chemical property
Hemihydrate is needle crystal (water). When 110 ℃, it become to anhydrous compounds. Melting point: 208 ℃, [alpha] 20D-35.2 (C = 2.8). When 25 ℃, water solubility was 4%, solubility is bigger in the hot water. Soluble in ethanol and acetone, slightly soluble in ethyl acetate.
Toxicity grading
toxication
Acute toxicity
Abdominal cavity-rat LDL0:4000 mg/kg
Flammability hazard characteristics
Combustible; Release acrid smoke fire
Storage and transport properties
Low temperature warehouse, ventilated, dry
Fire extinguishing agent
Water, carbon dioxide, dry powder, sand
Purification Methods
Crystallise the acid from water and dry it at 110o. [Beilstein 10 H 537, 10 I 271, 10 II 378, 10 III 2408, 10 IV 2259.]
Check Digit Verification of cas no
The CAS Registry Mumber 327-97-9 includes 6 digits separated into 3 groups by hyphens. The first part of the number,starting from the left, has 3 digits, 3,2 and 7 respectively; the second part has 2 digits, 9 and 7 respectively.
Calculate Digit Verification of CAS Registry Number 327-97:
(5*3)+(4*2)+(3*7)+(2*9)+(1*7)=69
69 % 10 = 9
So 327-97-9 is a valid CAS Registry Number.
InChI:InChI=1/C16H18O9/c17-9-3-1-8(5-10(9)18)2-4-13(20)25-12-7-16(24,15(22)23)6-11(19)14(12)21/h1-5,11-12,14,17-19,21,24H,6-7H2,(H,22,23)/b4-2+/t11-,12-,14-,16+/m1/s1
327-97-9Relevant articles and documents
Hepatoprotective constituents from the roots and stems of erycibe hainanesis
Song, Shuang,Li, Yixiu,Feng, Ziming,Jiang, Jianshuang,Zhang, Peicheng
, p. 177 - 184 (2010)
Eleven new diglycosides, erycibosides A-K (1-11), four new chlorogenic acid derivatives (14-17), and a new biscoumarin (18), together with 21 known compounds, have been isolated from an EtOH extract of the roots and stems of Erycibe hainanesis. Their structures were elucidated by means of spectroscopic methods and chemical evidence. Inhibitory activities of some of the compounds on D-galactosamine-induced cytotoxicity in WB-F344 rat hepatic epithelial stemlike cells were screened, and compounds 2, 6, 10, 18, and 32 showed potent hepatoprotective activities at concentrations of 1 × 10-5 to 1 × 10-4 M.
Identification and quantification of phenolic compounds from the forage legume sainfoin (Onobrychis viciifolia)
Regos, Ionela,Urbanella, Andrea,Treutter, Dieter
body text, p. 5843 - 5852 (2010/06/17)
Phenolic compounds of sainfoin (Onobrychis viciifolia) variety Cotswold Common are assumed to contribute to its nutritive value and bioactive properties. A purified acetone/water extract was separated by Sephadex LH-20 gel chromatography. Sixty-three phen
Synthesis of designed acylquinic acid derivatives involved in blue color development of hydrangea and their co-pigmentation effect
Toyama-Kato, Yuki,Kondo, Tadao,Yoshida, Kumi
, p. 239 - 254 (2008/03/12)
The blue sepal color of hydrangea may be developed by an unstable stipramolecular metal-complex pigment composed of delphinidin 3-glucoside (1), 5-O-caffeoylquinic acid (2) and 5-O-p-coumaroylquinic acid (3) as co-pigments and Al3+ in aqueous s