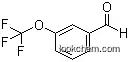
50823-91-1Relevant articles and documents
Radical C?H Trifluoromethoxylation of (Hetero)arenes with Bis(trifluoromethyl)peroxide
Dix, Stefan,Golz, Paul,Schmid, Jonas R.,Riedel, Sebastian,Hopkinson, Matthew N.
supporting information, p. 11554 - 11558 (2021/07/09)
Trifluoromethoxylated (hetero)arenes are of great interest for several disciplines, especially in agro- and medicinal chemistry. Radical C?H trifluoromethoxylation of (hetero)arenes represents an attractive approach to prepare such compounds, but the high cost and low atom economy of existing .OCF3 radical sources make them unsuitable for the large-scale synthesis of trifluoromethoxylated building blocks. Herein, we introduce bis(trifluoromethyl)peroxide (BTMP, CF3OOCF3) as a practical and efficient trifluoromethoxylating reagent that is easily accessible from inexpensive bulk chemicals. Using either visible light photoredox or TEMPO catalysis, trifluoromethoxylated arenes could be prepared in good yields under mild conditions directly from unactivated aromatics. Moreover, TEMPO catalysis allowed for the one-step synthesis of valuable pyridine derivatives, which have been previously prepared via multi-step approaches.
Photocatalytic trifluoromethoxylation of arenes and heteroarenes in continuous-flow
Cendón, Borja,Gulías, Moisés,Ho, Michelle,No?l, Timothy,Nyuchev, Alexander V.,Sambiagio, Carlo,Struijs, Job J. C.,Wan, Ting,Wang, Ying
supporting information, p. 1305 - 1312 (2020/07/10)
The first example of photocatalytic trifluoromethoxylation of arenes and heteroarenes under continuous-flow conditions is described. Application of continuous-flow microreactor technology allowed to reduce the residence time up to 16 times in comparison t
Radical Trifluoromethoxylation of Arenes Triggered by a Visible-Light-Mediated N?O Bond Redox Fragmentation
Jelier, Benson J.,Tripet, Pascal F.,Pietrasiak, Ewa,Franzoni, Ivan,Jeschke, Gunnar,Togni, Antonio
supporting information, p. 13784 - 13789 (2018/09/14)
A simple trifluoromethoxylation method enables non-directed functionalization of C?H bonds on a range of substrates, providing access to aryl trifluoromethyl ethers. This light-driven process is distinctly different from conventional procedures and occurs through an OCF3 radical mechanism mediated by a photoredox catalyst, which triggers an N?O bond fragmentation. The pyridinium-based trifluoromethoxylation reagent is bench-stable and provides access to synthetic diversity in lead compounds in an operationally simple manner.
Substituted N'-(arylcarbonyl)-benzhydrazides, N'-(arylcarbonyl)-benzylidene-hydrazides and analogs as activators of caspases and inducers of apoptosis and the use thereof
-
, (2008/06/13)
The present invention is directed to substituted N′-(arylcarbonyl)-benzhydrazides, N′-(arylcarbonyl)-benzylidene-hydrazides and analogs thereof, represented by the Formulae I and II: wherein Ar1, Ar2, and R1-R2 are defined herein. The present invention also relates to the discovery that compounds having Formulae I and II are activators of caspases and inducers of apoptosis. Therefore, the activators of caspases and inducers of apoptosis of this invention may be used to induce cell death in a variety of clinical conditions in which uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells occurs.
2-, 3-, and 4-(Trifluoromethoxy)phenyllithiums: Versatile intermediates offering access to a variety of new organofluorine compounds
Castagnetti, Eva,Schlosser, Manfred
, p. 691 - 695 (2007/10/03)
Consecutive treatment of (trifluoromethoxy)benzene with sec-butyllithium and electrophilic reagents affords previously inaccessible ortho-substituted derivatives in generally excellent yields. 2-(Trifluoromethoxy)phenyllithium acts as the key intermediate. The 3- and 4-isomers can readily be generated from the corresponding 3- and 4-bromo precursors by halogen-metal interconversion with butyllithium or tertbutyllithium. Upon trapping of the 2-, 3- and 4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyllithiums with 11 different electrophiles the expected products were formed in generally high yields. Only the attempted nucleophilic addition of 2-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyllithium to oxirane did not succeed. This failure is tentatively attributed to a lowering of the nucleophilicity by fluorine-lithium interactions. Conformationally restricted analogs - i.e., 2,2-difluoro-1,3-benzodioxol-4-phenyllithium and its 5-fluoro- and 5-bromo-substituted congeners - did indeed react smoothly with oxirane, affording the adducts in ordinary yields.
Phenylethylamine derivatives
-
, (2008/06/13)
Trifluoromethylthiophenylethylamine derivatives, made from the corresponding acid chlorides by successive reduction, condensation with nitroethane, reduction, and condensation with an amine, possess anorexigenic properties, unaccompanied by central stimulant activity or cardiovascular effects.
Phenyl propanones
-
, (2008/06/13)
Trifluoromethylthiophenylethylamine derivatives, made from the corresponding acid chlorides by successive reduction, condensation with nitroethane, reduction, and condensation with an amide, possess anorexigenic properties, unaccompanied by central stimulant activity or cardiovascular effects.