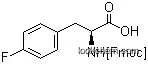
169243-86-1Relevant articles and documents
METHOD FOR PREPARING AROMATIC AMINO ACID DERIVATIVE
-
, (2022/05/13)
The present invention provides methods of efficiently producing various optically active aromatic amino acid derivatives by reacting, using an additive, a specific ester compound with an aromatic halide and zinc in the presence of a catalyst. The present invention also provides amino acid derivatives that can be produced by the methods.
Synthesis, in vitro biological activity, hydrolytic stability and docking of new analogs of BIM-23052 containing halogenated amino acids
Danalev, Dancho,Borisova, Desislava,Yaneva, Spaska,Georgieva, Maya,Balacheva, Anelia,Dzimbova, Tatyana,Iliev, Ivan,Pajpanova, Tamara,Zaharieva, Zdravka,Givechev, Ivan,Naydenova, Emilia
, p. 1581 - 1592 (2020/11/23)
One of the potent somatostatin analogs, BIM-23052 (DC-23-99) d-Phe-Phe-Phe-d-Trp-Lys-Thr-Phe-Thr-NH2, has established in vitro growth hormone inhibitory activity in nM concentrations. It is also characterized by high affinity to some somatostatin receptors which are largely distributed in the cell membranes of many tumor cells. Herein, we report the synthesis of a series of analogs of BIM-23052 containing halogenated Phe residues using standard solid-phase peptide method Fmoc/OtBu-strategy. The cytotoxic effects of the compounds were tested in vitro against two human tumor cell lines—breast cancer cell line and hepatocellular cancer cell line, as well as on human non-tumorigenic epithelial cell line. Analogs containing fluoro-phenylalanines are cytotoxic in μM range, as the analog containing Phe (2-F) showed better selectivity against human hepatocellular cancer cell line. The presented study also reveals that accumulation of halogenated Phe residues does not increase the cytotoxicity according to tested cell lines. The calculated selective index reveals different mechanisms of antitumor activity of the parent compound BIM-23052 and target halogenated analogs for examined breast tumor cell lines. All peptides tested have high antitumor activity against the HepG2 cell line (IC50 ≈ 100?μM and SI > 5) compared to breast cells. This is probably due to the high permeability of the cell membrane and the higher metabolic activity of hepatocytes. In silico docking studies confirmed that all obtained analogs bind well with the somatostatin receptors with preference to ssrt3 and ssrt5. All target compounds showed high hydrolytic stability at acid and neutral pH, which mimic physiological condition in stomach and human plasma.
LIGAND-CONTROLLED C(SP3)-H ARYLATION AND OLEFINATION IN SYNTHESIS OF UNNATURAL CHIRAL ALPHA AMINO ACIDS
-
, (2015/10/05)
The use of ligands to tune the reactivity and selectivity of transition metal-catalysts for C(-sp3)-H bond functionalization is a central challenge in synthetic organic chemistry. Herein, we report a rare example of catalyst-controlled C(sp3)-H arylation using pyridine and quinoline derivatives: the former promotes exclusive monoarylation, whereas the latter activates the catalyst further to achieve diarylation. Successive application of these ligands enables the sequential diarylation of a methyl group in an alanine derivative with two different aryl iodides, affording a wide range of β-Ar-p-Ar ' -cc-amino acids with excellent levels of diastereoselectivity (d.r. > 20:1). Both configurations of the β-chiral center can be accessed by choosing the order in which the aryl groups are installed. The use of a quinoline derivative as a ligand also enables C(sp3)-H olefination of a protected alanine.
Ligand-enabled β-C-H arylation of α-amino acids using a simple and practical auxiliary
Chen, Gang,Shigenari, Toshihiko,Jain, Pankaj,Zhang, Zhipeng,Jin, Zhong,He, Jian,Li, Suhua,Mapelli, Claudio,Miller, Michael M.,Poss, Michael A.,Scola, Paul M.,Yeung, Kap-Sun,Yu, Jin-Quan
, p. 3338 - 3351 (2015/03/30)
Pd-catalyzed β-C-H functionalizations of carboxylic acid derivatives using an auxiliary as a directing group have been extensively explored in the past decade. In comparison to the most widely used auxiliaries in asymmetric synthesis, the simplicity and practicality of the auxiliaries developed for C-H activation remains to be improved. We previously developed a simple N-methoxyamide auxiliary to direct β-C-H activation, albeit this system was not compatible with carboxylic acids containing α-hydrogen atoms. Herein we report the development of a pyridine-type ligand that overcomes this limitation of the N-methoxyamide auxiliary, leading to a significant improvement of β-arylation of carboxylic acid derivatives, especially α-amino acids. The arylation using this practical auxiliary is applied to the gram-scale syntheses of unnatural amino acids, bioactive molecules, and chiral bis(oxazoline) ligands.
Solid phase β-lactams synthesis using the Staudinger reaction, monitored by 19F NMR spectroscopy
Le Roy, Isabelle,Mouysset, Dominique,Mignani, Serge,Vuilhorgne, Marc,Stella, Lucien
, p. 3719 - 3727 (2007/10/03)
We report the use of 19F NMR as a simple means to monitor reactions on a solid phase. Multi-step sequences including protection, coupling, deprotection, condensation, cycloaddition and cleavage steps are described in the case of multicomponent reactions involving fluorinated α-aminoesters, aldehydes and acid chlorides.
Novel selective inhibitors of the interaction of individual nuclear hormone receptors with a mutually shared steroid receptor coactivator 2
Geistlinger, Timothy R.,Guy, R. Kiplin
, p. 6852 - 6853 (2007/10/03)
Nuclear hormone receptor (NR) signaling, currently a therapeutic target in multiple diseases, involves an ordered series of protein interactions to regulate transcription in response to changing hormone levels. Later steps in the process of ligand-dependent signaling are driven by a highly conserved interaction between the NRs and the steroid receptor coactivators (SRCs) that is effected by a conserved interaction motif (L1XXL2L3), known as an NR box. Using computational design and combinatorial chemistry, we have produced novel ∞-helical proteomimetics of the second NR box of SRC2 that exploit structural differences between human estrogen receptor ∞ (hER∞), human estrogen receptor β (hERβ), and human thyroid hormone receptor β (hTRβ). The resulting library sequentially replaced each leucine with non-natural side chains. Screening this library using a quantitative competition assay revealed compounds that selectively inhibit the interaction of SRC2-2 with each individual NR in preference to its interaction with the other NR. This approach generated highly selective compounds from one that had no specificity for a particular family member. These compounds represent the first family-member-selective competitive inhibitors of the protein interactions of transcription factors. Copyright