- CHLORINATED CAMPHENE
- Chlorinated diphenyl oxide
- Chlorinated paraffin
- Chlorinated Paraffins
- CHLORINATED POLYETHER POLYURETHAN
- Chlorinated Polyethylene
- Chlorinatedparaffin
- 8001-39-6Fats and Glyceridicoils, Japan wax
- 8001-40-9Fats and Glyceridicoils, vegetable, iodinated
- 8001-50-1Strobane
- 8001-54-5Benzalkonium chloride
- 8001-58-9Creosote
- 8001-67-0Oils, coffee
- 8001-75-0Ceresin
- 8001-78-3Castoroil, hydrogenated
- 8001-79-4Castor oil
- 80018-50-4Benzeneacetic acid,3-ethoxy-4-hydroxy-
Hot Products
- 104987-11-3Tacrolimus
- 141-53-7Sodium formate
- 8001-54-5Quaternary ammonium compounds, alkylbenzyldimethyl, chlorides
- 9003-39-8Povidone
- 10161-34-9Trenbolone acetate
- 402957-28-2Telaprevir
- 68-19-9Cyanocobalamin
- 7631-86-9Silicon dioxide
- 302-79-4Tretinoin
- 77-92-9Citric acid

|
Basic Information |

|
Post buying leads |

|
Suppliers |

|
Cas Database |

| Name |
CHLORINATED CAMPHENE |
EINECS | 232-283-3 | |
| CAS No. | 8001-35-2 | Density | 1.6 | |
| PSA | 0.00000 | LogP | 6.62720 | |
| Solubility | negligible | Melting Point |
65 - 90 C |
|
| Formula | C10H15Cl | Boiling Point | (decomposes) | |
| Molecular Weight | 170.6791 | Flash Point | 4°C | |
| Transport Information | N/A | Appearance | yellow waxy solid | |
| Safety |
Confirmed carcinogen with experimental carcinogenic and tumorigenic data. Human poison by ingestion and possibly other routes. Experimental poison by ingestion, intraperitoneal, and possibly other routes. Moderately toxic experimentally by inhalation and skin contact. Human systemic effects by ingestion and skin contact: somnolence, convulsions or effect on seizure threshold, coma, and allergic skin dermatitis. A skin irritant; absorbed through the skin. Experimental teratogenic and reproductive effects. Human mutation data reported. Liver injury has been reported. Lethal amounts of toxaphene can enter the body through the mouth, lungs, and skin. Systemic absorption of the insecticide is increased by the presence of digestible oils, and liquid preparations of the insecticide, which penetrate the skin more readily than do dusts and wettable powders. A toxic mixture of organochlorine pesticides stored to some extent in body fat. It resembles chlordane and, to some extent, camphor in its physiological action. It causes diffuse stimulation of the brain and spinal cord resulting in generalized convulsions of a tonic or clonic character. Death usually results from respiratory failure. Detoxification appears to occur in the liver. The lethal ingestion dose for humans is estimated to be 2–7 g, a toxicity of about four times that of DDT. At least seven human deaths have been reported due to toxaphene, all in children. Two families have been made ill by eating vegetables containing a large residue of toxaphene. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of Cl−. | |||
Analytical Methods: | For occupational chemical analysis use NIOSH: Chlorinated Camphene S67. |
Risk Codes | 21-25-37/38-40-50/53-67-65-38-11-36/37/38-39/23/24/25-23/24/25 | |
| Molecular Structure |
|
Hazard Symbols | Toxic by ingestion, inhalation, skin absorption; most uses prohibited. TLV: 0.5 mg/m3; STEL 1 mg/m3); animal carcinogen. | |
| Synonyms |
Alltox;Anatox; Camphechlor; Camphochlor; Canfeclor; Chlorinated camphene; Estonox;Geniphene; Hercules 3956; Kamfochlor; M 5055; Melipax; PCC; PChK; PChK(insecticide); PKhF; Phenacide; Phenatox; Polychlorocamphene; Strobane T;Toxakil; Toxaphen; Toxyphen |
Article Data | 3 |
CHLORINATED CAMPHENE Chemical Properties
Molecular Formula:C10H10Cl8
Molecular Weight:413.80
Melting Point:65 - 90°C
Water Solubility:Negligible
Storage temp.:2-8°C
Merck:13,9633
Appearance:Yellow waxy solid
CHLORINATED CAMPHENE's(8001-35-2) Synonyms: ALLTEX(R);CAMPHECHLOR;CAMPHECHLOR-(TOXAPHENE);GENIPHENE(R);HERCULES 3956(R);CHLORINATED CAMPHENE;POLYCHLOROBICYCLIC TERPENES;PHENETOX(R)
CHLORINATED CAMPHENE's(8001-35-2) Molecular Structure:
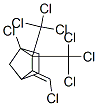
CHLORINATED CAMPHENE Toxicity Data With Reference
| 1. | skn-mam 500 mg MOD | JAMAAP JAMA, Journal of the American Medical Association. 149 (1952),1135. | ||
| 2. | mmo-sat 100 µg/plate | ENMUDM Environmental Mutagenesis. 8 (Suppl 7)(1986),1. | ||
| 3. | mma-sat 500 µg/plate | SCIEAS Science. 205 (1979),591. | ||
| 4. | sce-hmn:lym 10 µmol/L | ARTODN Archives of Toxicology. 52 (1983),221. | ||
| 5. | otr-mus:emb 12,400 µg/L | PMRSDJ Progress in Mutation Research. 5 (1985),659. | ||
| 6. | orl-hmn LDLo:28 mg/kg:CNS | 34ZIAG Toxicology of Drugs and Chemicals, Deichmann, W.B.,New York, NY.: Academic Press, Inc.,1969,598. | ||
| 7. | orl-man LDLo:29 mg/kg | CMEP** Clinical Memoranda on Economic Poisons US Dept. HEW, Public Health Service, Communicable Disease Center,Atlanta, GA.: 1956,1. | ||
| 8. | skn-hmn TDLo:657 mg/kg:SKN | CMEP** Clinical Memoranda on Economic Poisons US Dept. HEW, Public Health Service, Communicable Disease Center,Atlanta, GA.: 1956,1. | ||
| 9. | unr-man LDLo:44 mg/kg | 85DCAI Poisoning; Toxicology, Symptoms, Treatments. 2 (1970),73. | ||
| 10. | orl-rat LD50:50 mg/kg | & |
CHLORINATED CAMPHENE Consensus Reports
CHLORINATED CAMPHENE Safety Profile
A toxic mixture of organochlorine pesticides stored to some extent in body fat. It resembles chlordane and, to some extent, camphor in its physiological action. It causes diffuse stimulation of the brain and spinal cord resulting in generalized convulsions of a tonic or clonic character. Death usually results from respiratory failure. Detoxification appears to occur in the liver. The lethal ingestion dose for humans is estimated to be 2–7 g, a toxicity of about four times that of DDT. At least seven human deaths have been reported due to toxaphene, all in children. Two families have been made ill by eating vegetables containing a large residue of toxaphene. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of Cl−.
Safety Information of CHLORINATED CAMPHENE(8001-35-2)
Hazard Codes  T,N,
T,N, Xn,
Xn, F,Xi
F,Xi
Risk Statements 21-25-37/38-40-50/53-67-65-38-11-36/37/38-39/23/24/25-23/24/25
Safety Statements 36/37-45-60-61-62-33-16-36-26
RIDADR 2761
RTECS XW5250000
HazardClass 6.1(b)
PackingGroup III
CHLORINATED CAMPHENE Standards and Recommendations
ACGIH TLV: TWA 0.5 mg/m3; STEL 1 mg/m3 (skin); Animal Carcinogen
DFG MAK: Animal Carcinogen, Suspected Human Carcinogen
CHLORINATED CAMPHENE Analytical Methods
- About us - Payment - Contact us - Links - Help Center - Disclaimer
- SiteMap | Manufacturers | VIP Product | Suppliers | CAS | New CAS | Cas Database | Article Data | Chemical Catalog | Product Name
- ©2008 LookChem.com,License:ICP NO.:Zhejiang16009103 complaints:service@lookchem.com
- [Hangzhou]86-571-87562588,87562561,87562573 Our Legal adviser: Lawyer

