- 204206-08-6(E)-[4-(Acetylthio)-1-[2-cyclopropyl-1-(2-fluorophenyl)-2-oxoethyl]-3-piperidinylidene]acetic Acid Ethyl Ester (Mixture of Diastereomers)
- 2042-14-04-Methyl-3-nitrophenol
- 20422-68-84-ethyl-1,2-dimethyl-2,3,4a,5,6,7,8,8a-octahydroquinolin-4-ol
- 2042-27-5L-erythro-2-Pentulose
- 2042-37-72-Bromobenzonitrile
- 20423-99-8Pregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione,11,17-dihydroxy-, (11b)-
- 20424-00-4Pregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione,11-hydroxy-17-(1-oxopropoxy)-, (11b)-
- 204244-69-92-Pyridinemethanol,alpha,6-dimethyl-,(S)-(9CI)
- 204244-79-1Butanoic-3,3,4,4,4-d5acid, sodium salt (9CI)
- 204244-80-4Benzen-2,3,4,5-d4-amine,6-nitro- (9CI)
Hot Products
- 104987-11-3Tacrolimus
- 141-53-7Sodium formate
- 8001-54-5Quaternary ammonium compounds, alkylbenzyldimethyl, chlorides
- 9003-39-8Povidone
- 10161-34-9Trenbolone acetate
- 402957-28-2Telaprevir
- 68-19-9Cyanocobalamin
- 7631-86-9Silicon dioxide
- 302-79-4Tretinoin
- 77-92-9Citric acid

|
Basic Information |

|
Post buying leads |

|
Suppliers |

| Name |
Indibulin |
EINECS | N/A |
| CAS No. | 204205-90-3 | Density | 1.31 g/cm3 |
| PSA | 63.99000 | LogP | 4.63240 |
| Solubility | N/A | Melting Point |
N/A |
| Formula | C22H16ClN3O2 | Boiling Point | N/A |
| Molecular Weight | 389.83 | Flash Point | N/A |
| Transport Information | N/A | Appearance | N/A |
| Safety | Risk Codes | N/A | |
| Molecular Structure |
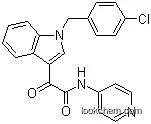
|
Hazard Symbols | N/A |
| Synonyms |
2-[1-[(4-chlorophenyl)methyl]indol-3-yl]-2-oxo-N-pyridin-4-yl-acetamide;2-(1-(4-Chlorophenylmethyl)-1H-indol-3-yl)-2-oxo-N-(pyridin-4-yl)acetamide;Indibulin [INN]; |
Indibulin Specification
The IUPAC name of Indibulin is 2-[1-[(4-chlorophenyl)methyl]indol-3-yl]-2-oxo-N-pyridin-4-ylacetamide . With the CAS registry number 204205-90-3, it is also named as N-(Pyridin-4-yl)-(1-(4-chlorobenzyl)indol-3-yl)glycoxylamide ; 2-(1-(4-Chlorophenylmethyl)-1H-indol-3-yl)-2-oxo-N-(pyridin-4-yl)acetamide ; D 24851 ; UNII-80K4H2RB8P ; ZIO-301 ; 1H-Indole-3-acetamide, 1-((4-chlorophenyl)methyl)-alpha-oxo-N-4-pyridinyl- .
Indibulin can be obtained by the following method. First, in DMSO , using NaH to concentrate 1H-indole (I) with 4-chlorobenzyl chloride (II) to get 1-(4-chlorobenzyl) indole (III) . Then, using oxalyl chloride treat 1-(4-chlorobenzyl) indole (III) in a hot aprotic solvent yielding the intermediate acid chloride (IV). Finally, this compound is treated with pyridin-4-amine (V) in the same solvent.

Indibulin is used in the treatment of cancer. Indibulin is a novel synthetic small molecule microtubule inhibitor, which destabilizes microtubules and has antitumor activity but does not exhibit neurotoxicity in preclinical animal studies. In the present study, it has been found that indibulin can discriminate between highly posttranslationally modified tubulin present in mature neuronal microtubules, and less-modified tubulin present in immature neuronal or nonneuronal microtubules. Due to the posttranslational modifications, the binding site of indibulin on mature neuronal microtubules seems to be inaccessible. There is a theory which is supported by the observation that indibulin did not disrupt the integrity of highly modified microtubules present in neurites of pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells. Because derivatives that have the pyridyl moiety replaced are not able to discriminate between highly and less-modified tubulins, the specificity of indibulin for unmodified microtubules seems to be dependent on the pyridyl moiety of indibulin .

