10.1073/pnas.18.7.490
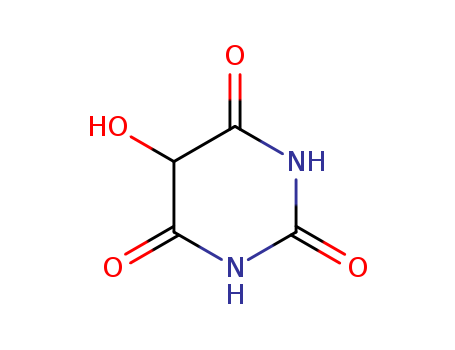
The research investigates the chemical properties and transformations of isovioluric acid and its derivatives. The purpose of the study is to explore the behavior of isovioluric acid, an unusual oxime of alloxan, and its reduction products. Key chemicals involved include isovioluric acid (VI), which is derived from isobarbituric acid through the action of nitrous acid. This compound exhibits unique properties such as oxidation of potassium iodide and formation of colored salts. The study also examines the reduction of isovioluric acid to isouramil (XI) using ammonium sulfide, which resembles dialuric acid in its chemical properties and can be converted into dialuric acid (XII) by hydrochloric acid. The research concludes that isovioluric acid and its derivatives display distinct behaviors compared to related compounds like alloxan and violuric acid, providing new insights into the chemistry of these uracil derivatives and their potential applications in the study of purine group compounds.