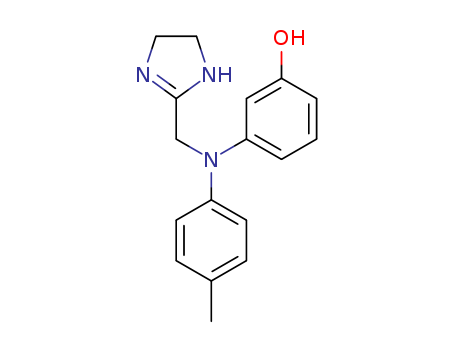
- Chemical Name:Phentolamine
- CAS No.:50-60-2
- Molecular Formula:C17H19N3O
- Molecular Weight:281.357
- Hs Code.:2933290090
- European Community (EC) Number:200-053-1
- UNII:Z468598HBV
- DSSTox Substance ID:DTXSID4023462
- Nikkaji Number:J4.105J
- Wikipedia:Phentolamine
- Wikidata:Q420360
- NCI Thesaurus Code:C62066
- RXCUI:8153
- Pharos Ligand ID:1AMCCN88WLZC
- Metabolomics Workbench ID:43005
- ChEMBL ID:CHEMBL597
- Mol file:50-60-2.mol
Synonyms:Fentolamin;Mesilate, Phentolamine;Mesylate, Phentolamine;Methanesulfonate, Phentolamine;Mono-hydrochloride, Phentolamine;Phentolamine;Phentolamine Mesilate;Phentolamine Mesylate;Phentolamine Methanesulfonate;Phentolamine Mono hydrochloride;Phentolamine Mono-hydrochloride;Regitine;Regityn;Rogitine;Z-Max