10.1021/op700270n
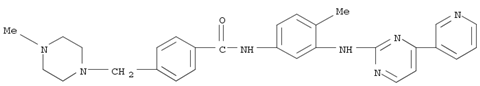
The study presents an improved method for synthesizing Imatinib and its analogues. Imatinib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor used to treat chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) and gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs). The researchers developed a more cost-effective and environmentally friendly approach to synthesize Imatinib by avoiding the use of toxic cyanamide and expensive palladium compounds. Key chemicals involved include enaminone, guanidine nitrate, and copper salts. Enaminone reacts with guanidine nitrate to form pyrimidinyl amine, a crucial intermediate. Copper salts are used as catalysts in the C-N bond-forming reaction to produce another key intermediate. The nitro compound intermediate is reduced using a N2H4·H2O/FeCl3/C system. The final steps involve acylation and amination reactions to yield Imatinib base. This method achieves good yields and avoids hazardous reagents, making it suitable for industrial applications.
10.1021/acs.oprd.9b00227
This study presents a new method for synthesizing Imatinib, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor used in treating chronic myeloid leukemia, through a C–N coupling reaction. The key chemicals involved include 4-(4-methylpiperazine-1-methyl)benzamide and N-(5-bromo-2-tolyl)-4-(3-pyridyl)pyrimidin-2-amine, which are coupled to form Imatinib. Nano-ZnO and KOH play crucial roles as catalysts in the hydrolysis of 4-(4-methylpiperazine-1-methyl)benzonitrile to produce the corresponding amide. The study highlights the efficiency and selectivity of nano-ZnO in this process. The new synthetic route avoids the production of genotoxic impurities, as classified by the FDA, and offers an environmentally friendly approach with a short reaction time and high purity of the final product.


 T,
T, N
N


