10.1039/c8nj00410b
The research focuses on the development and investigation of the catalytic activity of copper nanoparticles (CuNPs) supported on a Zinc oxide-polythiophene (ZnO-PTh) nanocomposite, denoted as CuNPs@ZnO-PTh. The purpose of this study was to create an efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally benign catalyst for the synthesis of propargylamine, tetra-substituted propargylamine, and pyrrolo[1,2-a]quinolines through A3 and KA2 coupling reactions. The researchers used a variety of chemicals in the synthesis process, including zinc chloride, sodium hydroxide, sodium dodecyl sulfate, thiophene, ferric chloride, copper nitrate trihydrate, and hydrazine hydrate. The conclusions drawn from the study highlight the high catalytic performance of the CuNPs@ZnO-PTh catalyst, which was attributed to its high surface area and the synergistic effect of both CuNPs and ZnO-PTh. The catalyst demonstrated excellent activity, selectivity, and recyclability, with the reactions yielding high product yields (up to 98%) in ethylene glycol, a green and biodegradable solvent, under microwave irradiation. The study concludes that this protocol is more efficient and sustainable compared to existing commercial methods.
10.1021/acs.orglett.7b02132
The research focuses on the development of a novel three-step domino transformation involving the aza-Michael-inverse electron-demand-hetero-Diels?Alder/retro-Diels?Alder (ihDA/rDA) reaction between primary and secondary propargylamine derivatives and 3-vinyl-1,2,4-triazines. The purpose of this study is to access polysubstituted tetrahydro-1,6-naphthyridine scaffolds, which are of significant interest in pharmaceutical industries due to their potential biological activities. The researchers successfully developed a straightforward method to synthesize these complex molecular structures, highlighting the versatility of 3-vinyl-1,2,4-triazines as both Michael acceptors and 4π components in the ihDA/rDA sequence. The study concluded that this approach offers a unique and efficient pathway to synthesize diversely substituted tetrahydro-1,6-naphthyridines, which could be valuable in drug discovery programs.
10.1021/ol201962n
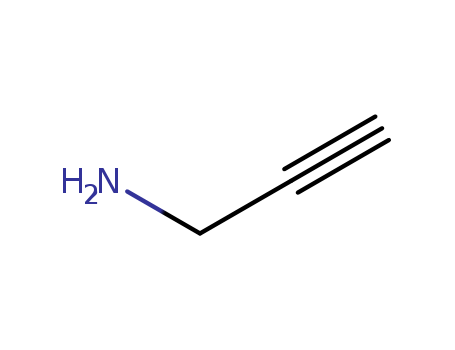
The research aims to develop a new method for synthesizing a diverse collection of benzofused sultams, which are cyclic sulfonamides with potential applications in drug discovery. The study employs a reaction pairing strategy involving a triad of reactions: sulfonylation, SNAr addition, and Mitsunobu alkylation. By varying the order of these reactions and using different building blocks such as o-fluorobenzenesulfonyl chlorides, amines, and alcohols, the researchers were able to generate a variety of tricyclic and bicyclic benzofused sultams. Key chemicals used include (S)-prolinol, propargylamine, (R)-(t)-3-hydroxypyrrolidine, and 2-piperidinemethanol. The study concludes that this approach allows for rapid and efficient synthesis of diverse sultam scaffolds in just 2-3 steps, making it highly suitable for high-throughput screening (HTS) in drug discovery. The synthesized compounds were found to be structurally diverse and unique compared to existing analogs, as demonstrated through chemical informatics analysis.


 F,
F, T
T

