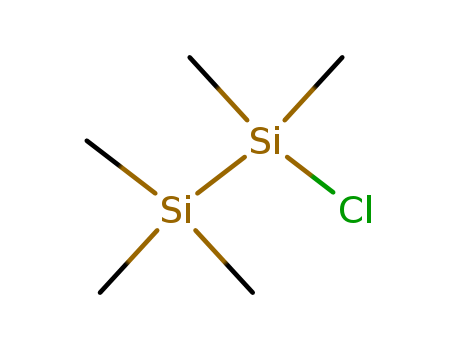
- Chemical Name:Chloropentamethyldisilane
- CAS No.:1560-28-7
- Molecular Formula:C5H15ClSi2
- Molecular Weight:166.798
- Hs Code.:
- European Community (EC) Number:216-330-5
- UNII:BVL5P5SYR7
- DSSTox Substance ID:DTXSID6061781
- Nikkaji Number:J46.580A
- Wikidata:Q63393307
- Mol file:1560-28-7.mol
Synonyms:Chloropentamethyldisilane;1560-28-7;Pentamethylchlorodisilane;Disilane, chloropentamethyl-;chloro-dimethyl-trimethylsilylsilane;Disilane, 1-chloro-1,1,2,2,2-pentamethyl-;1-chloro-1,1,2,2,2-pentamethyldisilane;BVL5P5SYR7;EINECS 216-330-5;chloropentamethyl disilane;C5H15ClSi2;UNII-BVL5P5SYR7;C5-H15-Cl-Si2;SCHEMBL947173;Chloropentamethyldisilane, 97%;DTXSID6061781;AMY42237;BAA56028;MFCD00456692;AKOS028108468;AS-49498;C3431;I10994;Q63393307


 F,
F,  C
C


