10.1016/S0040-4039(99)02175-9
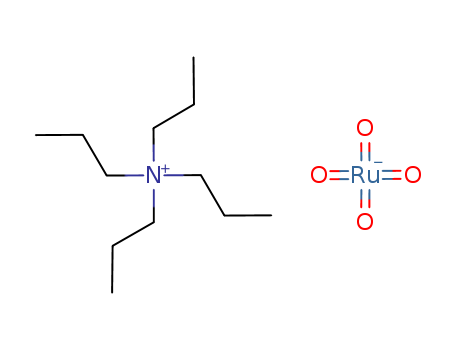
The research focuses on the stereocontrolled total synthesis of (±)-dysidiolide, a marine sesterterpenoid isolated from the Caribbean sponge Dysidia etheria de Laubenfels. Dysidiolide has been shown to inhibit protein phosphatase cdc25A and the growth of certain cancer cell lines. The synthesis involves an intramolecular Diels–Alder reaction as the key step. Key chemicals used in the process include cyclohexenone, LDA (lithium diisopropylamide), vinylmagnesium bromide, thiophenol, DIBAL-H (diisobutylaluminum hydride), mCPBA (meta-chloroperoxybenzoic acid), propiolic acid, DCC (dicyclohexylcarbodiimide), DMAP (4-dimethylaminopyridine), TBDMS-Cl (tert-butyldimethylsilyl chloride), imidazole, PON-Cl (bis(dimethylamino)phosphoryl chloride), TPAP (tetrapropylammonium perruthenate), NMO (N-methylmorpholine N-oxide), and various reagents for protection and deprotection steps such as TBDMS (tert-butyldimethylsilyl) and benzyl groups. The synthesis also involves several steps of oxidation, reduction, alkylation, and cross-coupling reactions to achieve the final product.