10.1039/c39820000769
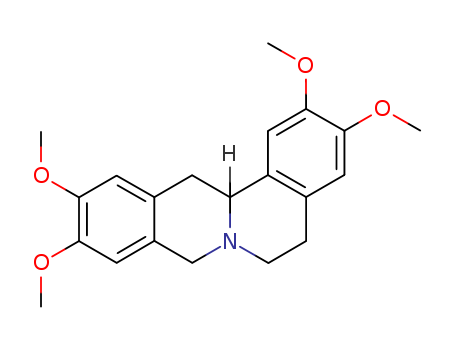
The research presents a novel synthesis of the isoquinoline alkaloids, (±)-xylopinine and (±)-laudanosine, through the nucleophilic addition of an organosilicon compound to a carbon-nitrogen double bond. The synthesis process involves several key steps and chemicals. Initially, 3,4-dimethoxybenzyltrimethylsilane (1) is prepared from 3,4-dimethoxybenzyl chloride and trimethylsilyl chloride via a Grignard reaction. This compound is then brominated to yield the 6-bromo-derivative (2). Subsequent reactions include the formation of benzaldehyde (3) using lithium and N,N'-dimethylformamide, followed by the conversion to a secondary amine (4) via reduction with sodium borohydride. The amine (4) is then transformed into the formamide (5), which undergoes a Bischler-Napieralski reaction to form the 3,4-dihydroisoquinolinium salt (6). The final step involves an intramolecular cyclisation using caesium fluoride to produce (±)-xylopinine (8). Additionally, an intermolecular version of this silicon-mediated addition yields (±)-laudanosine (11) under more forcing conditions. The trimethylsilyl group plays a crucial role in these reactions, remaining inert to fluoride anion but facilitating the cyclisation process.