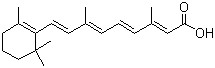
- Chemical Name:Tretinoin
- CAS No.:302-79-4
- Deprecated CAS:56573-65-0,7005-78-9,187175-63-9,7005-78-9
- Molecular Formula:C20H28O2
- Molecular Weight:300.441
- Hs Code.:29362100
- European Community (EC) Number:206-129-0
- NSC Number:759631,122758
- UNII:5688UTC01R
- DSSTox Substance ID:DTXSID7021239
- Nikkaji Number:J1.313.469C,J2.378.058E,J494.243D,J528.606I,J623.910B,J690.379G,J1.518K,J646.157C,J646.158A,J970.183D
- Wikipedia:Tretinoin
- Wikidata:Q29417
- NCI Thesaurus Code:C900,C2398
- RXCUI:10753
- Pharos Ligand ID:AAM7T1JPHW13
- Metabolomics Workbench ID:29042
- ChEMBL ID:CHEMBL38
- Mol file:302-79-4.mol
Synonyms:(2E,4E,6E,8E)-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexenyl)nona-2,4,6,8-tetraenoate;all-trans-beta-Retinoic acid;Vitamin A acid;Tretinoine (French) (EINECS);Retin A;trans-Retinoic acid;all-trans-Vitamin A1 acid;Acide retinoique (French) (DSL);2,4, 6,8-Nonatetranoic acid, 3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6, 6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-, (2E, 4E, 6E, 8E)-;all-trans-Retinoate;AGN 100335;Vitamin A acid sodium salt;Vitamin A1 acid, all-trans-;ATRA;Retin-A;Vesnaroid;Tretin M;all-(E)-Retinoic acid;Retinoic acid, sodium salt;beta-Retinoic acid;Cordes Vas;Aberel;Tretinoin, all-trans-;Retionic acid;Dermairol;Eudyna;Aknefug;Retinoate;all-trans-Retinoic acid;Retacnyl;Tretinoin (all-trans retinoic acid );Tretinoin USP26;


 T,
T, Xn
Xn


