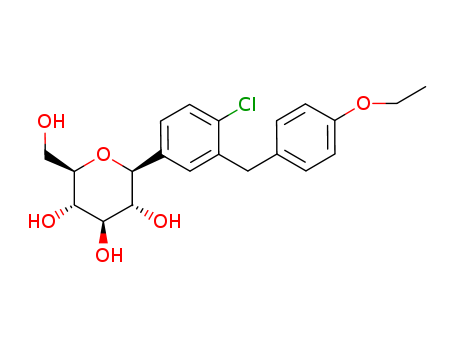
- Chemical Name:Dapagliflozin
- CAS No.:461432-26-8
- Molecular Formula:C21H25ClO6
- Molecular Weight:408.879
- Hs Code.:
- European Community (EC) Number:639-683-0
- UNII:1ULL0QJ8UC
- DSSTox Substance ID:DTXSID20905104
- Nikkaji Number:J2.928.717A
- Wikipedia:Dapagliflozin
- Wikidata:Q409898
- NCI Thesaurus Code:C78126
- RXCUI:1488564
- Pharos Ligand ID:2NSHZBU641RM
- Metabolomics Workbench ID:144441
- ChEMBL ID:CHEMBL429910
- Mol file:461432-26-8.mol
Synonyms:(2S,3R,4R,5S,6R)-2-(4-chloro-3-(4-ethoxybenzyl)phenyl)-6- (hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-3,4,5-triol;2-(3-(4-ethoxybenzyl)-4-chlorophenyl)-6-hydroxymethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-3,4,5-triol;BMS 512148;BMS-512148;BMS512148;dapagliflozin;Farxiga;forxiga