- Butyl 3-hydroxypropanoate
- Butyl 3-sulfanylpropanoate
- Butyl 4,4-bis(tert-butyldioxy)valerate
- Butyl 4-aminobenzoate
- Butyl 4-bromobutyrate
- Butyl 7-oxabicyclo[4.1.0]heptane-1-carboxylate
- Butyl chloroformate
- Butyl decyl phthalate
- Butyl D-glucoside
- Butyl hexanoate
- 942582-15-2Walsuronoid B
- 942603-46-5Proline, 5-oxo-1-(phenylmethyl)-,ethyl ester
- 942618-26-0Pyrrolidine,3-(2-methoxyethoxy)-, (3R)-
- 94262-08-5Carbanilic acid,4-[2-(diethylamino)acetamido]-3,5-dimethyl-, propyl ester (7CI)
- 942631-65-41H-Pyrazole-3-carboxylicacid, 1-(1-methylethyl)-
- 94265-95-93-Buten-2-ol,4-bicyclo[2.2.1]hept-5-en-2-yl-3-methyl-
- 94265-96-01H-2-Benzopyran,3,4,4a,7,8,8a-hexahydro-3,3,6,7-tetramethyl-, (4aa,7a,8aβ)- (9CI)
- 94266-06-53,5-Pyridinedicarboxylicacid, 4-butyl-1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-, 3,5-diethyl ester
- 94266-07-63,5-Pyridinedicarboxylicacid, 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-propyl-, 3,5-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl) ester
- 94266-34-9Heptadecanoic acid,magnesium salt (2:1)
Hot Products
- 104987-11-3Tacrolimus
- 141-53-7Sodium formate
- 8001-54-5Quaternary ammonium compounds, alkylbenzyldimethyl, chlorides
- 9003-39-8Povidone
- 10161-34-9Trenbolone acetate
- 402957-28-2Telaprevir
- 68-19-9Cyanocobalamin
- 7631-86-9Silicon dioxide
- 302-79-4Tretinoin
- 77-92-9Citric acid

|
Basic Information |

|
Post buying leads |

|
Suppliers |

|
Cas Database |

| Name |
Butyl 4-aminobenzoate |
EINECS | 202-317-1 |
| CAS No. | 94-25-7 | Density | 1.078 g/cm3 |
| PSA | 52.32000 | LogP | 2.80690 |
| Solubility | Insoluble in water | Melting Point |
57-58 °C(lit.) |
| Formula | C11H15NO2 | Boiling Point | 325.7 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Weight | 193.246 | Flash Point | 184.6 °C |
| Transport Information | N/A | Appearance | yellow powder |
| Safety | 26-36/37-36 | Risk Codes | 36/37/38-43 |
| Molecular Structure |
|
Hazard Symbols |
 Xi Xi
|
| Synonyms |
Benzoicacid, p-amino-, butyl ester (6CI,7CI,8CI);4-(Butoxycarbonyl)aniline;4-Aminobenzoic acid butyl ester;Benzoic acid, 4-amino-,butyl ester;Butambene;Butesin;Butesine;Butoform;Butsein;Butyl Keloform;Butylp-aminobenzoate;Butylcaine;Hemoride;NSC 128464;Planoform;Scuroform;Scuroforme;n-Butyl 4-aminobenzoate;n-Butyl p-aminobenzoate;p-Aminobenzoicacid butyl ester;p-Aminobenzoic acid n-butyl ester; |
Article Data | 29 |
Butyl 4-aminobenzoate Chemical Properties
Molecular Structure of Butamben (CAS NO.94-25-7):
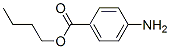
IUPAC Name: Butyl 4-aminobenzoate
Molecular Formula: C11H15NO2
Molecular Weight: 193.242300 g/mol
Melting Point: 57-58 °C(lit.)
Density: 1.078 g/cm3
Flash Point: 184.6 °C
Enthalpy of Vaporization: 56.78 kJ/mol
Boiling Point: 325.7 °C at 760 mmHg
Vapour Pressure: 0.000227 mmHg at 25 °C
XLogP3: 2.9
H-Bond Donor: 1
H-Bond Acceptor: 3
Rotatable Bond Count: 5
Tautomer Count: 3
Exact Mass: 193.110279
MonoIsotopic Mass: 193.110279
Topological Polar Surface Area: 52.3
Heavy Atom Count: 14
Canonical SMILES: CCCCOC(=O)C1=CC=C(C=C1)N
InChI: InChI=1S/C11H15NO2/c1-2-3-8-14-11(13)9-4-6-10(12)7-5-9/h4-7H,2-3,8,12H2,1H3
InChIKey: IUWVALYLNVXWKX-UHFFFAOYSA-N
EINECS:202-317-1
Product Categories: Aromatic Esters
Butyl 4-aminobenzoate Uses
Butamben (CAS NO.94-25-7) is mainly used to absorb UV in cosmetics. It is also used as intermediates in organic synthesis.
Butyl 4-aminobenzoate Toxicity Data With Reference
| 1. | ipr-mus LD50:67 mg/kg | JMCMAR Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 17 (1974),900. |
Butyl 4-aminobenzoate Consensus Reports
Reported in EPA TSCA Inventory.
Butyl 4-aminobenzoate Safety Profile
Hazard Codes:  Xi
Xi
Risk Statements: 36/37/38-43
R36/37/38:Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin.
R43:May cause sensitization by skin contact.
Safety Statements: 26-36/37-36
S26: In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice.
S36/37:Wear suitable protective clothing and gloves.
S36:Wear suitable protective clothing.
WGK Germany: 3
RTECS: DG1530000
Hazardous Substances Data: 94-25-7(Hazardous Substances Data)
Poison by intraperitoneal route. An allergen. See also ESTERS and AMINES. Combustible when exposed to heat or flame. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes such as NOx.
Butyl 4-aminobenzoate Specification
Butamben (CAS NO.94-25-7) is also named as 4-(Butoxycarbonyl)aniline ; 4-14-00-01130 (Beilstein Handbook Reference) ; 4-Aminobenzoic acid butyl ester ; AI3-02284 ; BRN 1211465 ; Benzoic acid, 4-amino-, butyl ester ; Benzoic acid, p-amino-, butyl ester ; Butesin ; Butesine ; Butoform ; Butyl 4-aminobenzoate ; Butyl keloform ; Butyl p-aminobenzoate ; Butylcaine ; Butylester kyseliny p-aminobenzoove ; Butylester kyseliny p-aminobenzoove [Czech] ; CCRIS 5891 ; HSDB 4245 ; N-Butyl p-aminobenzoate ; NSC 128464 ; Planoform ; Scuroform ; Scuroforme ; UNII-EFW857872Q ; n-Butyl p-aminobenzoate ; p-Aminobenzoic acid butyl ester . Butamben (CAS NO.94-25-7) is yellow powder. It is insoluble in water and soluble in acid, alcohol, chloroform, ether and fatty oils. It can slowly hydrolyze when boiled in water. It also will hydrolyze under high and low pH conditions. Butamben may be sensitive to light and air. Butamben is an aminophenyl ester derivative. Amines are chemical bases. They neutralize acids to form salts plus water. These acid-base reactions are exothermic. Amines may be incompatible with isocyanates, halogenated organics, peroxides, phenols (acidic), epoxides, anhydrides, and acid halides. Flammable gaseous hydrogen is generated by amines in combination with strong reducing agents, such as hydrides. The amount of heat that is evolved per mole of amine in a neutralization is largely independent of the strength of the amine as a base. Esters react with acids to liberate heat along with alcohols and acids. Strong oxidizing acids may cause a vigorous reaction that is sufficiently exothermic to ignite the reaction products. Heat is also generated by the interaction of esters with caustic solutions. Flammable hydrogen is generated by mixing esters with alkali metals and hydrides. Flash point data for Butamben are not available. It is probably combustible.

