10.1246/cl.1988.1415
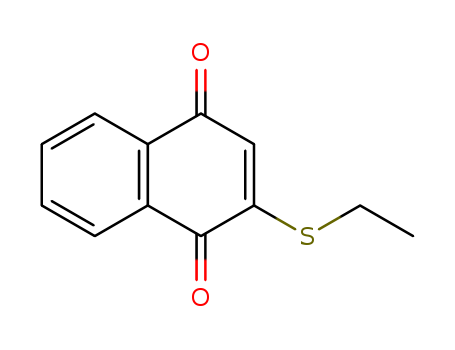
The research investigates the regioselective addition of lithium enolates to thio-substituted 1,4-naphthoquinones, aiming to develop a convenient synthesis route for naphthofuran-4,9-dione ring systems, which are biologically important naturally-occurring quinones. Key chemicals used include 2-phenylthio-1,4-naphthoquinone (1a), 2-ethylthio-1,4-naphthoquinone (1b), lithium enolates (2a-c), and HMPA. The study found that the addition of lithium enolates to thio-substituted 1,4-naphthoquinones selectively occurred at the 1,4-position, yielding 2-(2-oxoalkyl)-3-phenylthio-1,4-naphthoquinones (4a-d) in excellent yields. The thio-substituted group at the 2-position of the parent 1,4-naphthoquinone was crucial for determining the regiochemistry. Furthermore, the researchers successfully transformed one of the products, 2-(2-oxo-2-phenylethyl)-3-phenylthio-1,4-naphthoquinone (4c), into a naphthofuran-4,9-dione ring system through bromination and subsequent treatment with triethylamine. The study concludes that the regioselective 1,4-addition of lithium enolates to thio-substituted 1,4-naphthoquinones provides an efficient method for synthesizing naphthofuran-4,9-dione derivatives, and further research on synthesizing naturally-occurring cytotoxic naphthofuran-4,9-diones is ongoing.