10.1021/jm00108a035
This research aimed to explore the impact of modifying the hydrophobic/hydrophilic balance at a specific site of an aminoglycoside antibiotic, specifically kanamycin B, by chemically modifying its 6" position through substitution with various groups including halogens, pseudohalogens, amino, amido, thioalkyl, and alkoxy groups. The study sought to understand how these modifications affected the antibacterial activity and toxicity of the derivatives. The conclusions drawn from the research indicated that only derivatives with small substituents in position 6", such as chloro, bromo, azido, amino, and methylcarbamido, showed acceptable antibacterial activity. A negative correlation was observed between the size of the 6" substituent and antibacterial activity against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative organisms sensitive to kanamycin B. The chemicals used in the process included kanamycin B, tert-butoxycarbonyl (BOC) as an N-protective group, 2,4,6-triisopropylbenzenesulfonyl chloride (TIBS-Cl) for sulfonylation, various nucleophiles for substitution reactions, and a range of reagents for the synthesis of different 6"-substituted kanamycin B derivatives.
10.1021/jo00180a005
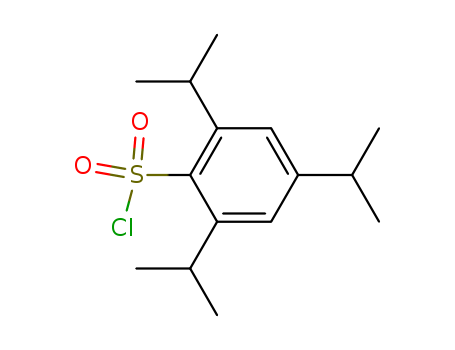
The research focuses on the selective monoarenesulfonation of sucrose, specifically the reaction with 2,4,6-triisopropylbenzenesulfonyl chloride (tripsyl chloride), which preferentially occurs at the 6'-OH group, yielding 6'-O-tripsylsucrose (2a) with a 39% yield without the need for chromatography. The study aimed to determine the substitution patterns at positions 6, 6', and 1' of sucrose and to establish the relative reactivities of the primary hydroxyl groups at these positions. The conclusions drawn from the research include the successful synthesis and characterization of 6'-O-tripsylsucrose and other related compounds, as well as the determination of the reactivity ratios of the primary hydroxyl groups (6':6:1' = 3.5:1.0:0.16).


 C
C


