10.1016/j.bmc.2019.05.026
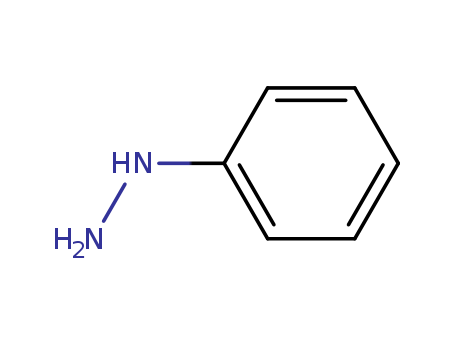
The research focuses on the synthesis and evaluation of new pyrazolopyrimidine derivatives as potential inhibitors of Leishmania amazonensis arginase, an enzyme crucial for polyamine biosynthesis in the parasite. Six derivatives with varying substituents at the 4-position of the phenyl group were synthesized and tested for their inhibitory activity against recombinant L. amazonensis arginase (LaARG). The synthesis involved reactions of phenylhydrazine with malononitrile, formic acid, and phosphorous oxychloride to obtain the desired compounds, which were then confirmed through techniques like NMR, IR, EI-MS, and HRMS. The biological evaluation included determining the IC50 values, kinetic analysis of enzyme inhibition, and molecular docking studies to understand the interaction of these compounds with LaARG. Additionally, the compounds were assessed for their cytotoxicity on mammalian macrophages and their anti-leishmanicidal activity against L. amazonensis amastigotes. The study utilized various analytical methods such as high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) for purity assessment and molecular modeling for structural analysis of the enzyme-inhibitor complexes.
10.1016/j.tetasy.2008.09.009
The research aimed to evaluate the influence of a sterically less demanding substituent at C(2) on the regioselectivity of Fischer indolization and to gain insight into the stereolability of pyrrolocarbazoles obtained from β-amino ketones. The study concluded that the α-carbon of the amino ester in polycyclic proline analogues showed stereolability in an acetic medium at 80–90°C, and there is a possibility of epimerization or racemization in pyrrolo[3,2-c] and pyrrolo[2,3-b]carbazoles when working with acetic or p-toluenesulfonic acid, as these compounds are prone to retro-Pictet Spengler and fragmentation processes, leading to the loss of their stereochemical integrity. Key chemicals used in the process included enantiopure 2-methoxycarbonyl-cis-octahydroindol-6-ones, acetic acid (AcOH), p-toluenesulfonic acid (TsOH), phenylhydrazine, and L-tyrosine as the chiral starting material.
10.1055/s-2007-977452
The research focuses on the stereoselective synthesis of novel D5-androstenoarylpyrazoline derivatives using BF3·OEt2-induced intramolecular 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition. The purpose of this study was to investigate the electronic effects of different phenyl substituents on cyclization reactions and to synthesize potentially bioactive androstenopyrazolines, which are known for their pharmacological effects such as analgesic, antipyretic, antirheumatic, anti-inflammatory, and antidiabetic activities. The researchers used D-seco-pregnene aldehyde as a starting material, which was reacted with phenylhydrazine or its para-substituted derivatives to form phenylhydrazones. These phenylhydrazones were then subjected to BF3·OEt2-catalyzed intramolecular cyclization to yield pyrazoline-fused D5-androstene derivatives. The study concluded that the stereoselective synthesis of androstenopyrazolines can be achieved through this method, with the efficacy of pyrazoline formation being strongly influenced by substituents on the phenyl moiety and the reaction conditions. Key chemicals used in the process include D-seco-pregnene aldehyde, phenylhydrazine, para-substituted phenylhydrazines, and BF3·OEt2 as the Lewis acid catalyst.
10.1246/bcsj.36.1272
The study investigates the condensation reactions of isopropylpyrido[3,2-d]tropolones. The researchers explored various reactions involving these compounds. For instance, 8-isopropyl-2-methylpyrido[3,2-d]tropolone and 9-isopropyl-2-methylpyrido[3,2-d]tropolone reacted with benzaldehyde to produce 8-isopropyl-2-styrylpyrido[3,2-d]tropolone (VIa) and 9-isopropyl-2-styrylpyrido[3,2-d]tropolone (VIb) respectively. The compounds Va, Vb, and Vc, which are derivatives of isopropylpyrido[3,2-d]tropolones, reacted with o-phenylenediamine in acetic acid to yield quinoxaline derivatives such as the quinoxalo derivative of 8-isopropylpyrido[3,2-d]tropolone (VIIla) and the quinoxalo derivative of 8-isopropyl-2-methylpyrido[3,2-d]tropolone (VIIIb). Additionally, the reaction of 8-isopropyl-2-methylpyrido[3,2-d]tropolone (XIb) with phenylhydrazine in acetic acid resulted in the formation of yellow crystals (XIIb) with a pyrido[3,2-d]indolo[2,3-b]tropone structure. The study also attempted to prepare quaternary salts of 8-isopropylpyrido[3,2-d]tropolones by reaction with methyl iodide, ethyl iodide, and ethyl p-toluenesulfonate, but these attempts were unsuccessful. The researchers concluded that the condensation products have specific structures based on their observations and spectral data analysis.
10.1021/jo00299a031
The research aimed to synthesize pentaleno[2,1-b:5,4-b']diindoles, which are complex organic compounds, using a combination of the Weiss reaction and the Fischer indole cyclization. The purpose was to prepare hexahydro-5,11-dihydropentaleno[2,1-b:5,4-b']diindoles and convert them into various 6,12-disubstituted derivatives. Despite numerous attempts, the researchers were unable to successfully convert these intermediates into bis(indo1o-substituted)pentalenes 5 or 6, as all attempts resulted in decomposition or ring scission products. The chemicals used in this process included phenylhydrazine, hydrochloric acid, selenium dioxide, phenylselenol, zinc iodide, and various solvents and reagents for chromatography and spectroscopic analysis. The conclusions drawn from the research were that while the diindole perhydropentalenes could be synthesized, the stabilization provided by the indole units in the targeted pentalenes was insufficient to prevent decomposition, suggesting that the benzene rings in dibenzopentalenes offer more effective stabilization than the indole units.
10.1016/S0008-6215(00)81064-2
The research investigates the reduction products and bromodeoxy derivatives of dehydro-L-ascorbic acid phenylhydrazone (1), aiming to explore its synthetic potential and utility as a precursor to nitrogen heterocycles. Key chemicals used include sodium borohydride for reduction, hydrogen bromide for bromination, and reagents like phenylhydrazine, semicarbazide, and thiosemicarbazide for further derivatization. The study found that reduction of compound 1 with sodium borohydride yielded L-xylo-2-hexulosono-1,4-lactone phenylhydrazone (2), which was further acetylated to produce 5O-acetyl-3,6-anhydro-L-xylo-2-hexulosono-1,4-lactone phenylhydrazone (3). Bromination of 1 resulted in 5,6-dibromo-5,6-dideoxy-L-xylo-2,3-hexodiulosono-1,4-lactone phenylhydrazone (5), which could be reacted with various hydrazines to form bis(hydrazones) and semicarbazones. The conclusions highlight the versatility of dehydro-L-ascorbic acid phenylhydrazone as a synthetic intermediate for creating diverse nitrogen-containing compounds.


 T,
T, N
N


