- Angiotensin
- Angiotensin acetate
- Angiotensin acetate
- Angiotensin I human acetate salt hydrate
- Angiotensin I, 5-L-isoleucine-
- Angiotensin II
- Angiotensin II antipeptide
- Angiotensin II,5-L-isoleucine-6-(4-amino-L-phenylalanine)-
- Angiotensin III,N2-(N-methylglycyl)-4-L-isoleucine-7-L-alanine- (9CI)
- 14074-80-7Zinc,[5,10,15,20-tetraphenyl-21H,23H-porphinato(2-)-kN21,kN22,kN23,kN24]-, (SP-4-1)-
- 140-75-0Benzenemethanamine,4-fluoro-
- 14075-53-7Potassium tetrafluoroborate
- 140-76-12-Methyl-5-vinylpyridine
- 140-77-2Cyclopentanepropanoicacid
- 14077-72-6Pyrimidine,2,4,6-trichloro-5-octyl-
- 14077-84-02,4,6(1H,3H,5H)-Pyrimidinetrione,5-heptyl-
- 140-79-4Piperazine,1,4-dinitroso-
- 14080-23-02-Cyanopyrimidine
- 14080-34-3Pyrimidine,2-methyl-5-nitro-
Hot Products
- 104987-11-3Tacrolimus
- 141-53-7Sodium formate
- 8001-54-5Quaternary ammonium compounds, alkylbenzyldimethyl, chlorides
- 9003-39-8Povidone
- 10161-34-9Trenbolone acetate
- 402957-28-2Telaprevir
- 68-19-9Cyanocobalamin
- 7631-86-9Silicon dioxide
- 302-79-4Tretinoin
- 77-92-9Citric acid

|
Basic Information |

|
Post buying leads |

|
Suppliers |

| Name |
Angiotensin |
EINECS | 215-804-9 |
| CAS No. | 1407-47-2 | Density | 1.48g/cm3 |
| PSA | 493.22000 | LogP | 3.83280 |
| Solubility | N/A | Melting Point |
N/A |
| Formula | C62H89N17O14 | Boiling Point | °Cat760mmHg |
| Molecular Weight | 1046.19 | Flash Point | °C |
| Transport Information | N/A | Appearance | powder |
| Safety | Poison by intravenous route. An experimental teratogen. Other experimental reproductive effects. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes. | Risk Codes | N/A |
| Molecular Structure |
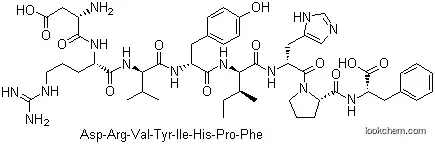
|
Hazard Symbols | N/A |
| Synonyms |
Angiotonin |
Angiotensin Chemical Properties
IUPAC Name: (3S)-3-Amino-4-[[(2S)-5-(diaminomethylideneamino)-1-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S,3S)-1-[[(2S)-1-[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-1-hydroxy-1-oxo-3-phenylpropan-2-yl]carbamoyl]pyrrolidin-1-yl]-3-(1H-imidazol-5-yl)-1-oxopropan-2-yl]amino]-3-methyl-1-oxopentan-2-yl]amino]-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1-oxopropan-2-yl]amino]-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl]amino]-1-oxopentan-2-yl]amino]-4-oxobutanoic acid
The MF of Hypertensin (CAS NO.1407-47-2) is C50H71N13O12.
.gif)
The MW of Hypertensin (CAS NO.1407-47-2) is 1046.19.
Synonyms of Hypertensin (CAS NO.1407-47-2): 5-L-Valine-angiotensin II amide ; Hypertensinamide ; L-Asparaginyl-L-arginyl-L-valyl-L-tyrosyl-L-valyl-L-histidyl-L-prolyl-L-phenylalanin ; 1-L-Asparagine-5-L-valineangiotensin II
Angiotensin History
Hypertensin was independently isolated in Indianapolis and Argentina in the late 1930s (as 'Angiotonin' and 'Hypertensin' respectively) and subsequently characterised and synthesized by groups at the Cleveland Clinic and Ciba laboratories in Basel, Switzerland.
Angiotensin Uses
Hypertensin (CAS NO.1407-47-2) is an oligopeptide in the blood that causes vasoconstriction, increased blood pressure, and release of aldosterone from the adrenal cortex. It is a hormone and a powerful dipsogen. It plays an important role in the renin-angiotensin system.
Angiotensin Production
It is derived from the precursor molecule angiotensinogen, a serum globulin produced in the liver.
Angiotensin Toxicity Data With Reference
| 1. | scu-ham TDLo:200 µg/kg (female 8 D post):TER | LIFSAK Life Sciences. 8 (1969),525. | ||
| 2. | scu-ham TDLo:20 µg/kg (female 8 D post):REP | LIFSAK Life Sciences. 8 (1969),525. | ||
| 3. | ivn-rat LDLo:8 mg/kg | 27ZIAQ Drug Dosages in Laboratory Animals-A Handbook C.D. Barnes and L.G. Eltherington,Berkeley, CA.: Univ. of California Press,1973,43. |
Angiotensin Safety Profile
Poison by intravenous route. An experimental teratogen. Other experimental reproductive effects. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes.
Angiotensin Specification
Hypertensin, a protein, causes blood vessels to constrict, and drives blood pressure up. It is part of the renin-angiotensin system, which is a major target for drugs that lower blood pressure. Hypertensin also stimulates the release of aldosterone from the adrenal cortex. Aldosterone promotes sodium retention in the distal nephron, in the kidney, which also drives blood pressure up.
Hypertensin I (CAS# 11128-99-7) is formed by the action of renin on angiotensinogen. Renin is produced in the kidneys in response to both decreased intra-renal blood pressure at the juxtaglomerular cells, or decreased delivery of Na+ and Cl- to the macula densa. If more Na+ is sensed, renin release is decreased.
Renin cleaves the peptide bond between the leucine (Leu) and valine (Val) residues on angiotensinogen, creating the ten amino acid peptide (des-Asp) angiotensin I (CAS# 9041-90-1).
Hypertensin I appears to have no biological activity and exists solely as a precursor to angiotensin 2.
Hypertensin I is converted to angiotensin II through removal of two terminal residues by the enzyme angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE, or kinase), which is found predominantly in the capillaries of the lungHypertensin II is degraded to angiotensin III by angiotensinases that are located in red blood cells and the vascular beds of most tissues. It has a half-life in circulation of around 30 seconds, while in tissue, it may be as long as 15–30 minutes.
Hypertensin III has 40% of the pressor activity of Angiotensin II, but 100% of the aldosterone-producing activity.
Hypertensin IV is a hexapeptide which, like angiotensin III, has some lesser activity.

