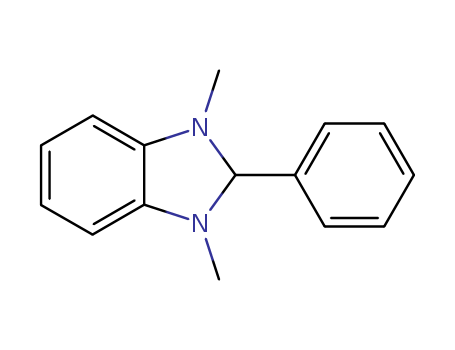
- Chemical Name:1,3-Dimethyl-2-phenylbenzimidazoline
- CAS No.:3652-92-4
- Molecular Formula:C15H16N2
- Molecular Weight:224.305
- Hs Code.:2933990090
- DSSTox Substance ID:DTXSID90190025
- Nikkaji Number:J69.240I
- Wikidata:Q83062276
- Mol file:3652-92-4.mol
Synonyms:3652-92-4;1,3-Dimethyl-2-phenylbenzimidazoline;1,3-Dimethyl-2-phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-benzo[d]imidazole;1,3-dimethyl-2-phenyl-2H-benzimidazole;Benzimidazoline, 1,3-dimethyl-2-phenyl-;1,3-Dimethyl-1,3-dihydro-2-phenyl-2H-benzimidazole;C15H16N2;ChemDiv3_000319;SCHEMBL993337;DTXSID90190025;HMS1473O11;AKOS021983201;CCG-103118;IDI1_019637;NCGC00176113-01;BS-51709;LS-33227;CS-0098800;FT-0699621;E77041;A902544;SR-01000389068;SR-01000389068-1;1,3-dimethyl-2-phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-benzimidazole