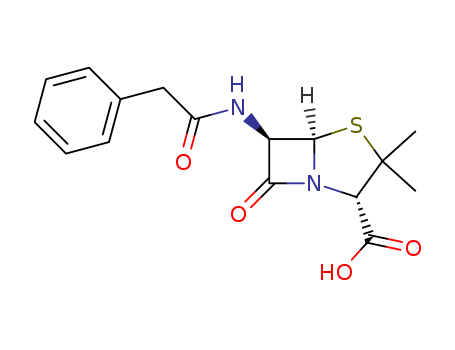
- Chemical Name:Penicillin G
- CAS No.:61-33-6
- Molecular Formula:C16H18N2O4S
- Molecular Weight:334.396
- Hs Code.:32041900
- European Community (EC) Number:200-506-3
- UNII:Q42T66VG0C
- DSSTox Substance ID:DTXSID5046934
- Nikkaji Number:J2.342F
- Wikipedia:Benzylpenicillin
- Wikidata:Q258450
- NCI Thesaurus Code:C61883
- RXCUI:7980
- Metabolomics Workbench ID:43291
- ChEMBL ID:CHEMBL29
- Mol file:61-33-6.mol
Synonyms:Benpen;Benzylpenicillin;Benzylpenicillin Potassium;Coliriocilina;Crystapen;Or-pen;Parcillin;Pekamin;Pengesod;Penibiot;Penicilina G Llorente;Penicillin G;Penicillin G Jenapharm;Penicillin G Potassium;Penicillin G Sodium;Penicillin Grünenthal;Penilevel;Peniroger;Pfizerpen;Sodiopen;Sodipen;Sodium Benzylpenicillin;Sodium Penicillin;Unicilina;Ursopen;Van-Pen-G


 Xn
Xn


