10.1021/jo010860d
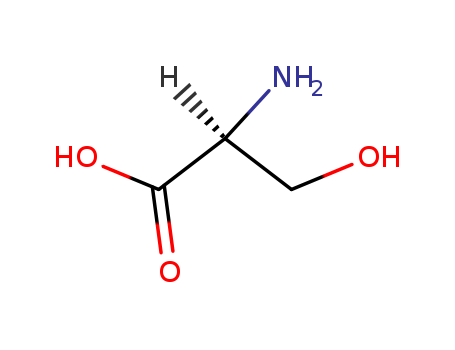
This study presents an asymmetric synthetic approach for the production of enantiomerically pure 3-phenylaziridine-2-carboxylate 7, a key intermediate for the synthesis of α-phenyl-substituted cysteine, tryptophan, and serine derivatives. These novel amino acids are of great interest as they have the potential to enhance the bioactivity and selectivity of peptides by constraining their side chain conformations. The synthesis involves the Sharpless asymmetric dihydroxylation of trans-benzylcinnamate 1 to generate (2R,3S)-diol 2, which is then transformed through a series of reactions involving cyclic sulfite 3, cyclic sulfate 4, and azido alcohols 5 and 6 to ultimately afford the desired aziridine 7. Further reactions with nucleophiles such as 4-methoxybenzyl mercaptan, indole, and acetic acid form the target amino acid derivatives. The chemicals used in the study serve as starting materials, reagents, and solvents in the various synthetic steps, each playing a crucial role in the formation of intermediates and final products.
10.1016/S0040-4039(02)00632-9
The research investigates the stereoretentive C-C bond formations in aldol cyclisations of 1-(3-oxobutyryl) derivatives of L-4-oxaproline and L-proline isopropyl esters. The purpose of the study was to explore the possibility of simplifying the self-generation of stereocenters in the synthesis of β-C-substituted β-amino acids, a class of compounds with wide-ranging biological properties, by leveraging the chirality memory effects observed in enolate intermediates. The researchers concluded that the aldol cyclisations conducted on oxaproline and proline scaffolds demonstrated significant retention of configuration, extending the scope of stereoinductions attributable to axially chiral enolate intermediates. Key chemicals used in the process included L-serine, isopropyl esters, L-oxaproline, L-proline, diketene, triethylamine, and potassium cyanide, among others. The study's findings are significant as they provide insights into the role of axially chiral enolate intermediates in stereoselective synthesis and contribute to the development of more efficient methods for producing enantioenriched β-C-substituted β-amino acids embedded in heterocyclic frameworks.
10.1246/bcsj.54.1844
The study investigates the synthesis of oxazolidines, thiazolidines, and 5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-1H,3H-pyrrolo[1,2-c]oxazole (or thiazole)-1,3-diones from β-hydroxy- or β-mercapto-α-amino acid esters. Aromatic aldehydes such as benzaldehyde, p-anisaldehyde, p-chlorobenzaldehyde, and p-nitrobenzaldehyde are used to react with amino acid ethyl esters like L-serine, 3-phenyl-DL-serine, L-threonine, or L-cysteine to form oxazolidines or thiazolidines. These compounds can then be converted into oxazoles and thiazoles through dehydrogenation using N-bromosuccinimide. Acetylation of oxazolidines and thiazolidines leads to N-acetylderivatives, which can undergo cyclization in the presence of anhydrous ZnCl? to form the tetrahydro-pyrrolo[1,2-c]oxazole (or thiazole)-1,3-diones. The study also explores the interaction of oxazolidines and thiazolidines with p-nitrobenzaldehyde and piperidine to form Mannich bases. The IR spectra of the synthesized compounds are analyzed, showing characteristic shifts and absorptions related to functional groups such as the ester group and the oxazole or thiazole ring.
10.1002/hlca.19870700426
The study, titled "Stereoselective Alkylation at C(α) of Serine, Glyceric Acid, Threonine, and Tartaric Acid Involving Heterocyclic Enolates with Exocyclic Double Bonds," investigates the stereoselective alkylation of various chiral, non-racemic α-amino acids and their derivatives using heterocyclic enolates with exocyclic double bonds. The researchers converted these acids into methyl dioxolane, oxazoline, and oxazolidine carboxylates. These compounds were then deprotonated to form lithium enolates, which were stable enough to undergo alkylation with or without cosolvents like HMPA or DMPU. The products were obtained in good to excellent yields and with high diastereoselectivities, except for the tartrate-derived acetonide. The study demonstrated that the configuration of the products could be determined through NOE-NMR measurements and chemical correlation, revealing that the dioxolane-derived enolates were alkylated preferentially from the face already substituted, while the dihydrooxazol- and oxazolidine-derived enolates were alkylated from the opposite face. This work provides a method for constructing quaternary stereogenic centers without racemization, using readily available enantiomerically pure precursors like hydroxy- and amino-acids.
10.1016/j.tet.2018.04.082
The study presents a simplified method for beta-glycosylation of peptides, focusing on the activation of S-phenyl thioglycosides using N-iodosuccinimide and catalytic copper(I) triflate. This method effectively promotes beta-O-glycosylation at serine and threonine hydroxyls in "mono-," di-, and tripeptides, as well as beta-N-glycosylation of asparagine-containing peptides. A key advantage is the minimization of undesired amide O-glycosylation. The study also develops streamlined deprotection sequences based on global hydrogenolysis, leading to the parent glycopeptides. The core glycopeptide region for biological protein N-glycosylation has been synthesized, purified, and characterized. The research provides an efficient process for O- and N-glycosylation of peptides, which is beneficial for multistep preparations, especially those limited by material availability.
10.1021/jo0206824
The research focuses on the total syntheses of symbioramide derivatives, which are bioactive compounds with potential antileukemic properties, derived from L-serine. The study involves the preparation of various symbioramide derivatives, including (2S,3R,2′R,3′E)-N-(2′-hydroxy-3′-octadecenoyl)-dihydrosphingosine (1a) and its diastereomers (1b-d), by synthesizing the amino part (D-erythro-dihydrosphingosine) and acid parts ((2R,3E)-2-hydroxy-3-octadecenoic acid and its isomers) from L-serine and D-mannitol, respectively. The synthesized compounds were then assessed for their antileukemic activities against HL-60 and L-1210 cell lines using the MTT assay. The experiments utilized various reagents, protection and deprotection strategies, and purification techniques such as column chromatography. Analytical methods like specific rotation measurements, infrared spectroscopy (IR), nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), and high-resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS) were employed to characterize the synthesized compounds and assess their structures and purities. The results indicated that all symbioramide derivatives showed moderate antileukemic activities against L-1210 cells, with compound 1d being the most effective.
10.1021/ol1012789
The research focuses on the development of a novel two-step synthesis method for oxazole-4-carboxylates from aldehydes, utilizing 3-oxazoline-4-carboxylates as synthetic intermediates. The main content involves a one-pot condensation-oxidation of aldehydes with serine or threonine methyl ester to form 3-oxazoline-4-carboxylates, followed by oxidation to obtain the desired oxazole-4-carboxylates. The experiments employed various reactants, including aldehydes, serine or threonine methyl ester, DABCO, NCS, and different oxidizing agents such as NBS, K2CO3, and molecular sieves. The analyses used to monitor the reactions and characterize the products included thin-layer chromatography (TLC), and the synthesized compounds were confirmed through detailed spectroscopic data provided in the supporting information. This method offers a more efficient and straightforward approach to synthesize oxazole derivatives compared to the traditional three-step procedures, and it also explores the reactivity of 3-oxazoline-4-carboxylates with Grignard reagents, leading to the facile preparation of 4-keto-oxazole derivatives.


 Xi
Xi


