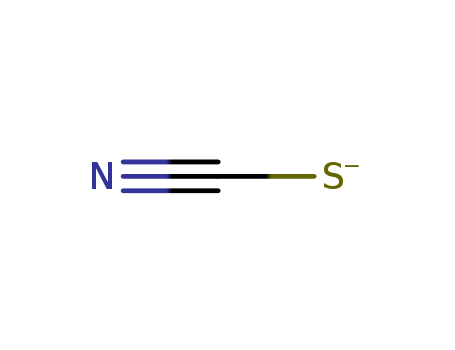- Chemical Name:Thiocyanate
- CAS No.:302-04-5
- Deprecated CAS:1111-68-8,37223-05-5,60168-45-8,60773-55-9,62476-95-3,69924-38-5,70874-95-2,81210-01-7
- Molecular Formula:CN S
- Molecular Weight:58.0837
- Hs Code.:
- European Community (EC) Number:222-571-7,671-005-9
- UNII:O748SU14OM
- DSSTox Substance ID:DTXSID8047763
- Nikkaji Number:J215.799C,J330.947I
- Wikipedia:Thiocyanate,Thallium thiocyanate
- Wikidata:Q60839
- Mol file:302-04-5.mol
Synonyms:thiocyanate;thiocyanate ion;thiocyanate ion (1-);thiocyanate ion (2-);Thiocyanogen ((SCN)2(1-))